一、项目概览
Dragonboat 是纯 Go 实现的(multi-group)Raft 库。
为应用屏蔽 Raft 复杂性,提供易于使用的 NodeHost 和状态机接口。该库(自称)有如下特点:
- 高吞吐、流水线化、批处理;
- 提供了内存/磁盘状态机多种实现;
- 提供了 ReadIndex、成员变更、Leader转移等管理端API;
- 默认使用 Pebble 作为 存储后端。
本次代码串讲以V3的稳定版本为基础,不包括GitHub上v4版本内容。
二、整体架构
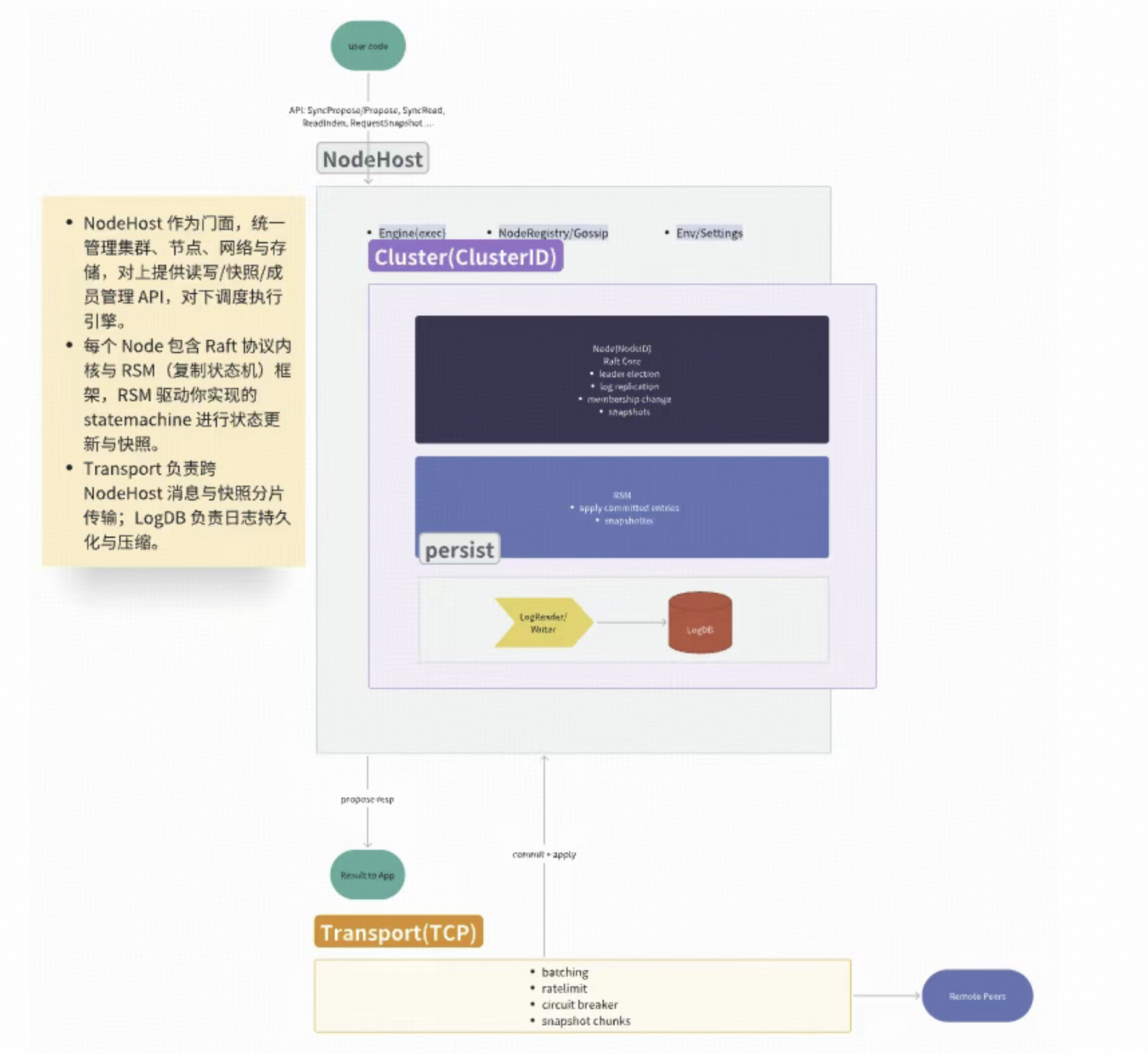
三、LogDB 统一存储
LogDB 模块是 Dragonboat 的核心持久化存储层,虽然模块名字有Log,但是它囊括了所有和存储相关的API,负责管理 Raft 协议的所有持久化数据,包括:
Raft状态 (RaftState)
Raft内部状态变更的集合结构
包括但不限于:
- ClusterID/NodeID: 节点ID
- RaftState: Raft任期、投票情况、commit进度
- EntriesToSave:Raft提案日志数据
- Snapshot:快照元数据(包括快照文件路径,快照大小,快照对应的提案Index,快照对应的Raft任期等信息)
- Messages:发给其他节点的Raft消息
- ReadyToReads:ReadIndex就绪的请求
引导信息 (Bootstrap)
type Bootstrap struct {
Addresses map[uint64]string // 初始集群成员
Join bool
Type StateMachineType
}
ILogDB的API如下:
type ILogDB interface {
BinaryFormat() uint32 // 返回支持的二进制格式版本号
ListNodeInfo() ([]NodeInfo, error) // 列出 LogDB 中所有可用的节点信息
// 存储集群节点的初始化配置信息,包括是否加入集群、状态机类型等
SaveBootstrapInfo(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, bootstrap pb.Bootstrap) error
// 获取保存的引导信息
GetBootstrapInfo(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64) (pb.Bootstrap, error)
// 原子性保存 Raft 状态、日志条目和快照元数据
SaveRaftState(updates []pb.Update, shardID uint64) error
// 迭代读取指定范围内的连续日志条目
IterateEntries(ents []pb.Entry, size uint64, clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64,
low uint64, high uint64, maxSize uint64) ([]pb.Entry, uint64, error)
// 读取持久化的 Raft 状态
ReadRaftState(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, lastIndex uint64) (RaftState, error)
// 删除指定索引之前的所有条目, 日志压缩、快照后清理旧日志
RemoveEntriesTo(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, index uint64) error
// 回收指定索引之前条目占用的存储空间
CompactEntriesTo(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, index uint64) (<-chan struct{}, error)
// 保存所有快照元数据
SaveSnapshots([]pb.Update) error
// 删除指定的快照元数据 清理过时或无效的快照
DeleteSnapshot(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, index uint64) error
// 列出指定索引范围内的可用快照
ListSnapshots(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, index uint64) ([]pb.Snapshot, error)
// 删除节点的所有相关数据
RemoveNodeData(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64) error
// 导入快照并创建所有必需的元数据
ImportSnapshot(snapshot pb.Snapshot, nodeID uint64) error
}
3.1索引键
存储的底层本质是一个KVDB (pebble or rocksdb),由于业务的复杂性,要统一各类业务key的设计方法,而且要降低空间使用,所以有了如下的key设计方案。
龙舟中key分为3类:
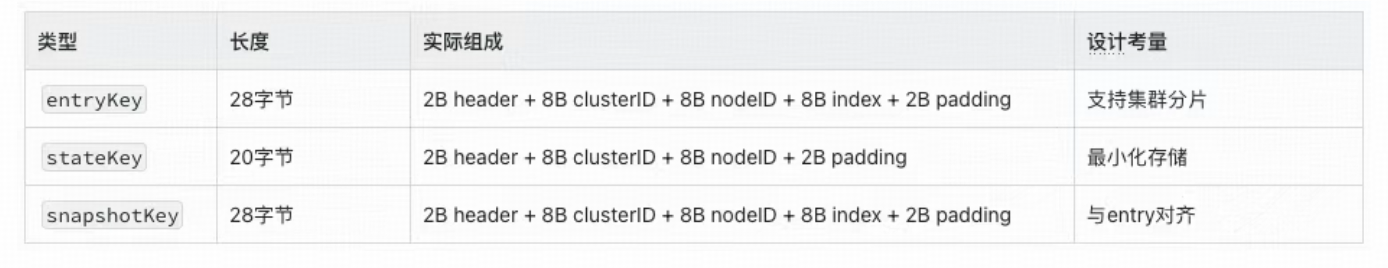 其中,2字节的header用于区分各类不同业务的key空间。
其中,2字节的header用于区分各类不同业务的key空间。
entryKeyHeader = [2]byte{0x1, 0x1} // 普通日志条目
persistentStateKey = [2]byte{0x2, 0x2} // Raft状态
maxIndexKey = [2]byte{0x3, 0x3} // 最大索引记录
nodeInfoKey = [2]byte{0x4, 0x4} // 节点元数据
bootstrapKey = [2]byte{0x5, 0x5} // 启动配置
snapshotKey = [2]byte{0x6, 0x6} // 快照索引
entryBatchKey = [2]byte{0x7, 0x7} // 批量日志
在key的生成中,采用了useAsXXXKey和SetXXXKey的方式,复用了data这个二进制变量,减少GC。
type Key struct {
data []byte // 底层字节数组复用池
key []byte // 有效数据切片
pool *sync.Pool // 似乎并没有什么用
}
func (k *Key) useAsEntryKey() {
k.key = k.data
}
type IReusableKey interface {
SetEntryBatchKey(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, index uint64)
// SetEntryKey sets the key to be an entry key for the specified Raft node
// with the specified entry index.
SetEntryKey(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, index uint64)
// SetStateKey sets the key to be an persistent state key suitable
// for the specified Raft cluster node.
SetStateKey(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64)
// SetMaxIndexKey sets the key to be the max possible index key for the
// specified Raft cluster node.
SetMaxIndexKey(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64)
// Key returns the underlying byte slice of the key.
Key() []byte
// Release releases the key instance so it can be reused in the future.
Release()
}
func (k *Key) useAsEntryKey() {
k.key = k.data
}
// SetEntryKey sets the key value to the specified entry key.
func (k *Key) SetEntryKey(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, index uint64) {
k.useAsEntryKey()
k.key[0] = entryKeyHeader[0]
k.key[1] = entryKeyHeader[1]
k.key[2] = 0
k.key[3] = 0
binary.BigEndian.PutUint64(k.key[4:], clusterID)
// the 8 bytes node ID is actually not required in the key. it is stored as
// an extra safenet - we don't know what we don't know, it is used as extra
// protection between different node instances when things get ugly.
// the wasted 8 bytes per entry is not a big deal - storing the index is
// wasteful as well.
binary.BigEndian.PutUint64(k.key[12:], nodeID)
binary.BigEndian.PutUint64(k.key[20:], index)
}
3.2变量复用IContext
IContext的核心设计目的是实现并发安全的内存复用机制。在高并发场景下,频繁的内存分配和释放会造成较大的GC压力,通过IContext可以实现:
-
键对象复用:通过GetKey()获取可重用的IReusableKey
-
缓冲区复用:通过GetValueBuffer()获取可重用的字节缓冲区
-
批量操作对象复用:EntryBatch和WriteBatch的复用
// IContext is the per thread context used in the logdb module. // IContext is expected to contain a list of reusable keys and byte // slices that are owned per thread so they can be safely reused by the // same thread when accessing ILogDB. type IContext interface { // Destroy destroys the IContext instance. Destroy() // Reset resets the IContext instance, all previous returned keys and // buffers will be put back to the IContext instance and be ready to // be used for the next iteration. Reset() // GetKey returns a reusable key. GetKey() IReusableKey // 这就是上文中的key接口 // GetValueBuffer returns a byte buffer with at least sz bytes in length. GetValueBuffer(sz uint64) []byte // GetWriteBatch returns a write batch or transaction instance. GetWriteBatch() interface{} // SetWriteBatch adds the write batch to the IContext instance. SetWriteBatch(wb interface{}) // GetEntryBatch returns an entry batch instance. GetEntryBatch() pb.EntryBatch // GetLastEntryBatch returns an entry batch instance. GetLastEntryBatch() pb.EntryBatch }
type context struct { size uint64 maxSize uint64 eb pb.EntryBatch lb pb.EntryBatch key *Key val []byte wb kv.IWriteBatch }
func (c *context) GetKey() IReusableKey { return c.key }
func (c *context) GetValueBuffer(sz uint64) []byte { if sz <= c.size { return c.val } val := make([]byte, sz) if sz < c.maxSize { c.size = sz c.val = val } return val }
func (c *context) GetEntryBatch() pb.EntryBatch { return c.eb }
func (c *context) GetLastEntryBatch() pb.EntryBatch { return c.lb }
func (c *context) GetWriteBatch() interface{} { return c.wb }
func (c *context) SetWriteBatch(wb interface{}) { c.wb = wb.(kv.IWriteBatch) }
3.3存储引擎封装IKVStore
IKVStore 是 Dragonboat 日志存储系统的抽象接口,它定义了底层键值存储引擎需要实现的所有基本操作。这个接口让 Dragonboat 能够支持不同的存储后端(如 Pebble、RocksDB 等),实现了存储引擎的可插拔性。
type IKVStore interface {
// Name is the IKVStore name.
Name() string
// Close closes the underlying Key-Value store.
Close() error
// 范围扫描 - 支持前缀遍历的迭代器
IterateValue(fk []byte,
lk []byte, inc bool, op func(key []byte, data []byte) (bool, error)) error
// 查询操作 - 基于回调的内存高效查询模式
GetValue(key []byte, op func([]byte) error) error
// 写入操作 - 单条记录的原子写入
SaveValue(key []byte, value []byte) error
// 删除操作 - 单条记录的精确删除
DeleteValue(key []byte) error
// 获取批量写入器
GetWriteBatch() IWriteBatch
// 原子提交批量操作
CommitWriteBatch(wb IWriteBatch) error
// 批量删除一个范围的键值对
BulkRemoveEntries(firstKey []byte, lastKey []byte) error
// 压缩指定范围的存储空间
CompactEntries(firstKey []byte, lastKey []byte) error
// 全量压缩整个数据库
FullCompaction() error
}
type IWriteBatch interface {
Destroy() // 清理资源,防止内存泄漏
Put(key, value []byte) // 添加写入操作
Delete(key []byte) // 添加删除操作
Clear() // 清空批处理中的所有操作
Count() int // 获取当前批处理中的操作数量
}
openPebbleDB是Dragonboat 中 Pebble 存储引擎的初始化入口,负责根据配置创建一个完整可用的键值存储实例。
// KV is a pebble based IKVStore type.
type KV struct {
db *pebble.DB
dbSet chan struct{}
opts *pebble.Options
ro *pebble.IterOptions
wo *pebble.WriteOptions
event *eventListener
callback kv.LogDBCallback
config config.LogDBConfig
}
var _ kv.IKVStore = (*KV)(nil)
// openPebbleDB
// =============
// 将 Dragonboat 的 LogDBConfig → Pebble 引擎实例
func openPebbleDB(
cfg config.LogDBConfig,
cb kv.LogDBCallback, // => busy通知:busy(true/false)
dir string, // 主数据目录
wal string, // WAL 独立目录(可空)
fs vfs.IFS, // 文件系统抽象(磁盘/memfs)
) (kv.IKVStore, error) {
//--------------------------------------------------
// 2️⃣ << 核心调优参数读入
//--------------------------------------------------
blockSz := int(cfg.KVBlockSize) // 数据块(4K/8K...)
writeBufSz := int(cfg.KVWriteBufferSize) // 写缓冲
bufCnt := int(cfg.KVMaxWriteBufferNumber) // MemTable数量
l0Compact := int(cfg.KVLevel0FileNumCompactionTrigger) // L0 层文件数量触发压缩的阈值
l0StopWrites := int(cfg.KVLevel0StopWritesTrigger)
baseBytes := int64(cfg.KVMaxBytesForLevelBase)
fileBaseSz := int64(cfg.KVTargetFileSizeBase)
cacheSz := int64(cfg.KVLRUCacheSize)
levelMult := int64(cfg.KVTargetFileSizeMultiplier) // 每层文件大小倍数
numLevels := int64(cfg.KVNumOfLevels)
//--------------------------------------------------
// 4️⃣ 构建 LSM-tree 层级选项 (每层无压缩)
//--------------------------------------------------
levelOpts := []pebble.LevelOptions{}
sz := fileBaseSz
for lvl := 0; lvl < int(numLevels); lvl++ {
levelOpts = append(levelOpts, pebble.LevelOptions{
Compression: pebble.NoCompression, // 写性能优先
BlockSize: blockSz,
TargetFileSize: sz, // L0 < L1 < ... 呈指数增长
})
sz *= levelMult
}
//--------------------------------------------------
// 5️⃣ 初始化依赖:LRU Cache + 读写选项
//--------------------------------------------------
cache := pebble.NewCache(cacheSz) // block缓存
ro := &pebble.IterOptions{} // 迭代器默认配置
wo := &pebble.WriteOptions{Sync: true} // ❗fsync强制刷盘
opts := &pebble.Options{
Levels: levelOpts,
Cache: cache,
MemTableSize: writeBufSz,
MemTableStopWritesThreshold: bufCnt,
LBaseMaxBytes: baseBytes,
L0CompactionThreshold: l0Compact,
L0StopWritesThreshold: l0StopWrites,
Logger: PebbleLogger,
FS: vfs.NewPebbleFS(fs),
MaxManifestFileSize: 128 * 1024 * 1024,
// WAL 目录稍后条件注入
}
kv := &KV{
dbSet: make(chan struct{}), // 关闭->初始化完成信号
callback: cb, // 上层 raft engine 回调
config: cfg,
opts: opts,
ro: ro,
wo: wo,
}
event := &eventListener{
kv: kv,
stopper: syncutil.NewStopper(),
}
// => 关键事件触发
opts.EventListener = pebble.EventListener{
WALCreated: event.onWALCreated,
FlushEnd: event.onFlushEnd,
CompactionEnd: event.onCompactionEnd,
}
//--------------------------------------------------
// 7️⃣ 目录准备
//--------------------------------------------------
if wal != "" {
fs.MkdirAll(wal) // 📁 为 WAL 单独磁盘预留
opts.WALDir = wal
}
fs.MkdirAll(dir) // 📁 主数据目录
//--------------------------------------------------
// 8️⃣ 真正的数据库实例化
//--------------------------------------------------
pdb, err := pebble.Open(dir, opts)
if err != nil { return nil, err }
//--------------------------------------------------
// 9️⃣ 🧹 资源整理 & 启动事件
//--------------------------------------------------
cache.Unref() // 去除多余引用,防止泄露
kv.db = pdb
// 🔔 手动触发一次 WALCreated 确保反压逻辑进入首次轮询
kv.setEventListener(event) // 内部 close(kv.dbSet)
return kv, nil
}
其中eventListener是对pebble 内存繁忙的回调,繁忙判断的条件有两个:
-
内存表大小超过阈值(95%)
-
L0 层文件数量超过阈值(L0写入最大文件数量-1)
func (l *eventListener) notify() { l.stopper.RunWorker(func() { select { case <-l.kv.dbSet: if l.kv.callback != nil { memSizeThreshold := l.kv.config.KVWriteBufferSize * l.kv.config.KVMaxWriteBufferNumber * 19 / 20 l0FileNumThreshold := l.kv.config.KVLevel0StopWritesTrigger - 1 m := l.kv.db.Metrics() busy := m.MemTable.Size >= memSizeThreshold || uint64(m.Levels[0].NumFiles) >= l0FileNumThreshold l.kv.callback(busy) } default: } }) }
3.4日志条目存储DB
db结构体是Dragonboat日志数据库的核心管理器,提供Raft日志、快照、状态等数据的持久化存储接口。是桥接了业务和pebble存储的中间层。
// db is the struct used to manage log DB.
type db struct {
cs *cache // 节点信息、Raft状态信息缓存
keys *keyPool // Raft日志索引键变量池
kvs kv.IKVStore // pebble的封装
entries entryManager // 日志条目读写封装
}
// 这里面的信息不会过期,叫寄存更合适
type cache struct {
nodeInfo map[raftio.NodeInfo]struct{}
ps map[raftio.NodeInfo]pb.State
lastEntryBatch map[raftio.NodeInfo]pb.EntryBatch
maxIndex map[raftio.NodeInfo]uint64
mu sync.Mutex
}
- 获取一个批量写容器
实现:
func (r *db) getWriteBatch(ctx IContext) kv.IWriteBatch {
if ctx != nil {
wb := ctx.GetWriteBatch()
if wb == nil {
wb = r.kvs.GetWriteBatch()
ctx.SetWriteBatch(wb)
}
return wb.(kv.IWriteBatch)
}
return r.kvs.GetWriteBatch()
}
降低GC压力
- 获取所有节点信息
实现:
func (r *db) listNodeInfo() ([]raftio.NodeInfo, error) {
fk := newKey(bootstrapKeySize, nil)
lk := newKey(bootstrapKeySize, nil)
fk.setBootstrapKey(0, 0)
lk.setBootstrapKey(math.MaxUint64, math.MaxUint64)
ni := make([]raftio.NodeInfo, 0)
op := func(key []byte, data []byte) (bool, error) {
cid, nid := parseNodeInfoKey(key)
ni = append(ni, raftio.GetNodeInfo(cid, nid))
return true, nil
}
if err := r.kvs.IterateValue(fk.Key(), lk.Key(), true, op); err != nil {
return []raftio.NodeInfo{}, err
}
return ni, nil
}
- 保存集群状态
实现:
type Update struct {
ClusterID uint64 // 集群ID,标识节点所属的Raft集群
NodeID uint64 // 节点ID,标识集群中的具体节点
State // 包含当前任期(Term)、投票节点(Vote)、提交索引(Commit)三个关键持久化状态
EntriesToSave []Entry // 需要持久化到稳定存储的日志条目
CommittedEntries []Entry // 已提交位apply的日志条目
MoreCommittedEntries bool // 指示是否还有更多已提交条目等待处理
Snapshot Snapshot // 快照元数据,当需要应用快照时设置
ReadyToReads []ReadyToRead // ReadIndex机制实现的线性一致读
Messages []Message // 需要发送给其他节点的Raft消息
UpdateCommit struct {
Processed uint64 // 已推送给RSM处理的最后索引
LastApplied uint64 // RSM确认已执行的最后索引
StableLogTo uint64 // 已稳定存储的日志到哪个索引
StableLogTerm uint64 // 已稳定存储的日志任期
StableSnapshotTo uint64 // 已稳定存储的快照到哪个索引
ReadyToRead uint64 // 已准备好读的ReadIndex请求索引
}
}
func (r *db) saveRaftState(updates []pb.Update, ctx IContext) error {
// 步骤1:获取写入批次对象,用于批量操作提高性能
// 优先从上下文中获取已存在的批次,避免重复创建
wb := r.getWriteBatch(ctx)
// 步骤2:遍历所有更新,处理每个节点的状态和快照
for _, ud := range updates {
// 保存 Raft 的硬状态(Term、Vote、Commit)
// 使用缓存机制避免重复保存相同状态
r.saveState(ud.ClusterID, ud.NodeID, ud.State, wb, ctx)
// 检查是否有快照需要保存
if !pb.IsEmptySnapshot(ud.Snapshot) {
// 快照索引一致性检查:确保快照索引不超过最后一个日志条目的索引
// 这是 Raft 协议的重要约束,防止状态不一致
if len(ud.EntriesToSave) > 0 {
lastIndex := ud.EntriesToSave[len(ud.EntriesToSave)-1].Index
if ud.Snapshot.Index > lastIndex {
plog.Panicf("max index not handled, %d, %d",
ud.Snapshot.Index, lastIndex)
}
}
// 保存快照元数据到数据库
r.saveSnapshot(wb, ud)
// 更新节点的最大日志索引为快照索引
r.setMaxIndex(wb, ud, ud.Snapshot.Index, ctx)
}
}
// 步骤3:批量保存所有日志条目
// 这里会调用 entryManager 接口的 record 方法,根据配置选择批量或单独存储策略
r.saveEntries(updates, wb, ctx)
// 步骤4:提交写入批次到磁盘
// 只有在批次中有实际操作时才提交,避免不必要的磁盘 I/O
if wb.Count() > 0 {
return r.kvs.CommitWriteBatch(wb)
}
return nil
}
- 保存引导信息
实现:
func (r *db) saveBootstrapInfo(clusterID uint64,
nodeID uint64, bs pb.Bootstrap) error {
wb := r.getWriteBatch(nil)
r.saveBootstrap(wb, clusterID, nodeID, bs)
return r.kvs.CommitWriteBatch(wb) // 提交至Pebble
}
func (r *db) saveBootstrap(wb kv.IWriteBatch,
clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64, bs pb.Bootstrap) {
k := newKey(maxKeySize, nil)
k.setBootstrapKey(clusterID, nodeID) // 序列化集群节点信息
data, err := bs.Marshal()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
wb.Put(k.Key(), data)
}
- 获取Raft状态
实现:
func (r *db) getState(clusterID uint64, nodeID uint64) (pb.State, error) {
k := r.keys.get()
defer k.Release()
k.SetStateKey(clusterID, nodeID)
hs := pb.State{}
if err := r.kvs.GetValue(k.Key(), func(data []byte) error {
if len(data) == 0 {
return raftio.ErrNoSavedLog
}
if err := hs.Unmarshal(data); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return nil
}); err != nil {
return pb.State{}, err
}
return hs, nil
}
3.5对外存储API实现
龙舟对ILogDB提供了实现:ShardedDB,一个管理了多个pebble bucket的存储单元。
var _ raftio.ILogDB = (*ShardedDB)(nil)
// ShardedDB is a LogDB implementation using sharded pebble instances.
type ShardedDB struct {
completedCompactions uint64 // 原子计数器:已完成压缩操作数
config config.LogDBConfig // 日志存储配置
ctxs []IContext // 分片上下文池,减少GC压力
shards []*db // 核心:Pebble实例数组
partitioner server.IPartitioner // 智能分片策略器
compactionCh chan struct{} // 压缩任务信号通道
compactions *compactions // 压缩任务管理器
stopper *syncutil.Stopper // 优雅关闭管理器
}
- 初始化过程
实现:
// 入口函数:创建并初始化分片日志数据库
OpenShardedDB(config, cb, dirs, lldirs, batched, check, fs, kvf):
// ===阶段1:安全验证===
if 配置为空 then panic
if check和batched同时为true then panic
// ===阶段2:预分配资源管理器===
shards := 空数组
closeAll := func(all []*db) { //出错清理工具
for s in all {
s.close()
}
}
// ===阶段3:逐个创建分片===
loop i := 0 → 分片总数:
datadir := pathJoin(dirs[i], "logdb-"+i) //数据目录
snapdir := "" //快照目录(可选)
if lldirs非空 {
snapdir = pathJoin(lldirs[i], "logdb-"+i)
}
shardCb := {shard:i, callback:cb} //监控回调
db, err := openRDB(...) //创建实际数据库实例
if err != nil { //创建失败
closeAll(shards) //清理已创建的
return nil, err
}
shards = append(shards, db)
// ===阶段5:核心组件初始化===
partitioner := 新建分区器(execShards数量, logdbShards数量)
instance := &ShardedDB{
shards: shards,
partitioner: partitioner,
compactions: 新建压缩管理器(),
compactionCh: 通道缓冲1,
ctxs: make([]IContext, 执行分片数),
stopper: 新建停止器()
}
// ===阶段6:预分配上下文&启动后台===
for j := 0 → 执行分片数:
instance.ctxs[j] = 新建Context(saveBufferSize)
instance.stopper.RunWorker(func() { //后台压缩协程
instance.compactionWorkerMain()
})
return instance, nil //构造完成
- 保存集群状态
实现:
func (s *ShardedDB) SaveRaftState(updates []pb.Update, shardID uint64) error {
if shardID-1 >= uint64(len(s.ctxs)) {
plog.Panicf("invalid shardID %d, len(s.ctxs): %d", shardID, len(s.ctxs))
}
ctx := s.ctxs[shardID-1]
ctx.Reset()
return s.SaveRaftStateCtx(updates, ctx)
}
func (s *ShardedDB) SaveRaftStateCtx(updates []pb.Update, ctx IContext) error {
if len(updates) == 0 {
return nil
}
pid := s.getParititionID(updates)
return s.shards[pid].saveRaftState(updates, ctx)
}
以sylas为例子,我们每个分片都是单一cluster,所以logdb只使用了一个分片,龙舟设计初衷是为了解放多cluster的吞吐,我们暂时用不上,tindb可以考虑:
四、总结
LogDB是Dragonboat重要的存储层实现,作者将Pebble引擎包装为一组通用简洁的API,极大方便了上层应用与存储引擎的交互成本。
其中包含了很多Go语言的技巧,例如大量的内存变量复用设计,展示了这个库对高性能的极致追求,是一个十分值得学习的优秀工程案例。
往期回顾
-
从数字到版面:得物数据产品里数字格式化的那些事
-
一文解析得物自建 Redis 最新技术演进
-
Golang HTTP请求超时与重试:构建高可靠网络请求|得物技术
-
RN与hawk碰撞的火花之C++异常捕获|得物技术
-
得物TiDB升级实践
文 /酒米
关注得物技术,每周更新技术干货
要是觉得文章对你有帮助的话,欢迎评论转发点赞~
未经得物技术许可严禁转载,否则依法追究法律责任。
</div>相关推荐
- 「第三届开放原子大赛」获奖队伍专访来啦!企业篇
- 从本体论到落地实践:制造业数字化转型的核心逻辑与工具选择 | 葡萄城技术团队
- 轻松搞定Excel公式错误:SpreadJS让表格开发不再头疼 | 葡萄城技术团队
- vivo GPU容器与 AI 训练平台探索与实践
- SQLShift V6.0 发布!函数迁移&达梦适配一步到位!
- Oinone × AI Agent 落地指南:别让 AI Agent 负责“转账”:用神经-符号混合架构把它从 Demo 拉进生产
- 借助 Okta 和 NGINX Ingress Controller 实现 K8s OpenID Connect 身份验证
- 同样是低代码,为什么有人扩容有人烂尾?答案藏在交付体系里-拆解 Oinone 的交付底座


