<span id="OSC_h2_1"></span> 1 概述
1.1 背景介绍
仓颉编程语言作为一款面向全场景应用开发的现代编程语言,通过现代语言特性的集成、全方位的编译优化和运行时实现、以及开箱即用的 IDE工具链支持,为开发者打造友好开发体验和卓越程序性能。
案例结合代码体验,让大家更直观的了解仓颉语言中的枚举类型与模式匹配。
1.2 适用对象
- 个人开发者
- 高校学生
1.3 案例时间
本案例总时长预计40分钟。
1.4 案例流程
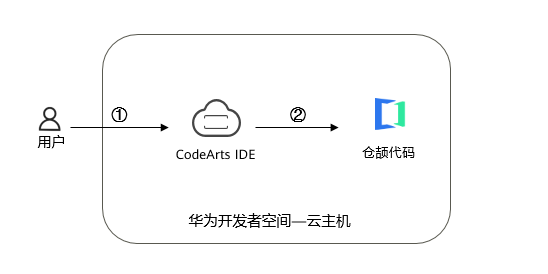
说明:
① 进入华为开发者空间,登录云主机;
② 使用CodeArts IDE for Cangjie编程和运行仓颉代码。
1.5 资源总览
| 资源名称 | 规格 | 单价(元) | 时长(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 开发者空间 – 云主机 | 鲲鹏通用计算增强型 kc2 | 4vCPUs | 8G | Ubuntu | 免费 | 40 |
仓颉之枚举类型与模式匹配的冒险之旅 👈👈👈体验最新完整版案例,点击这里。
2 运行测试环境准备
2.1 开发者空间配置
面向广大开发者群体,华为开发者空间提供一个随时访问的“开发桌面云主机”、丰富的“预配置工具集合”和灵活使用的“场景化资源池”,开发者开箱即用,快速体验华为根技术和资源。
领取云主机后可以直接进入华为开发者空间工作台界面,点击打开云主机 > 进入桌面连接云主机。没有领取在开发者空间根据指引领取配置云主机即可,云主机配置参考1.5资源总览。
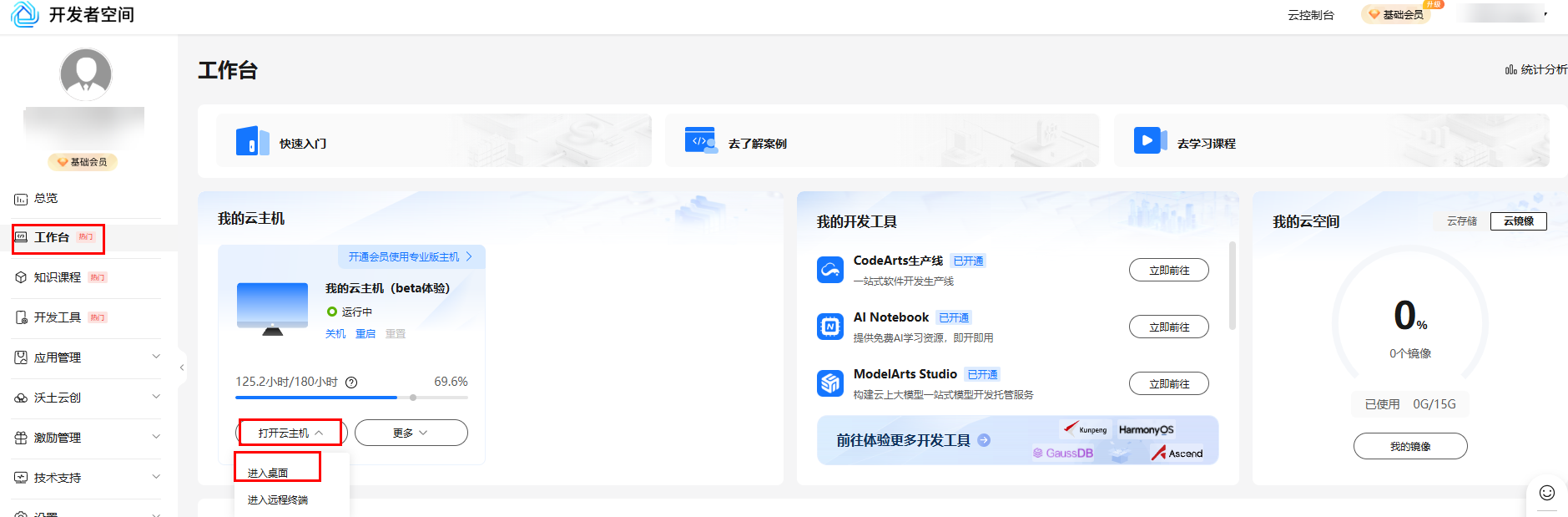

2.2 创建仓颉程序
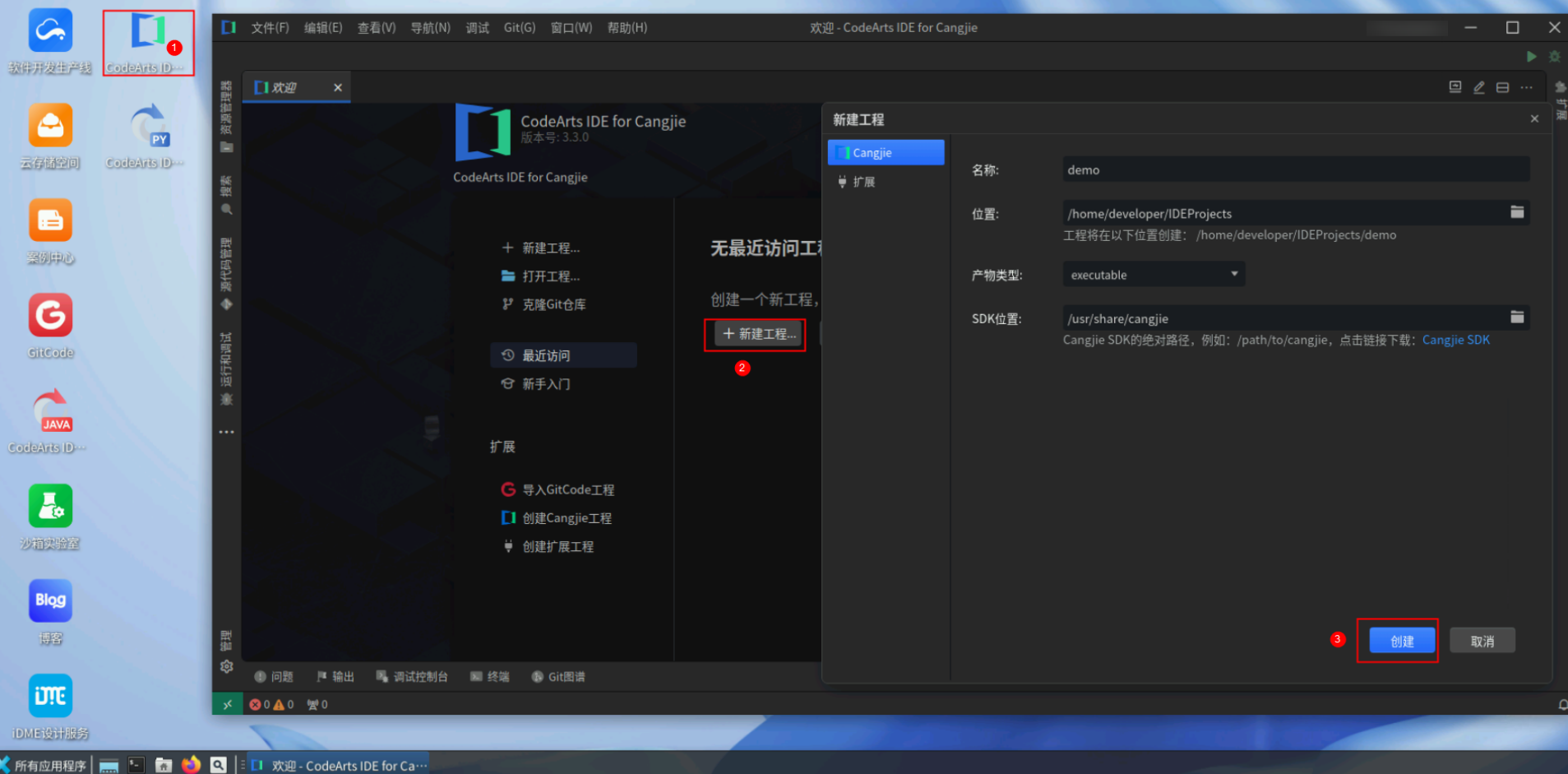
点击桌面CodeArts IDE for Cangjie,打开编辑器,点击新建工程,保持默认配置,点击创建。
产物类型说明:
- executable,可执行文件;
- static,静态库,是一组预先编译好的目标文件的集合;
- dynamic,动态库,是一种在程序运行时才被加载到内存中的库文件,多个程序共享一个动态库副本,而不是像静态库那样每个程序都包含一份完整的副本。
2.3 运行仓颉工程
创建完成后,打开src/main.cj,参考下面代码简单修改后,点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
<strong>package</strong> demo
<span style="color:#697070">// 第一个仓颉程序</span>
main(): Int64 {
<span style="color:#397300">println</span>(<span style="color:#880000">"hello world"</span>)
<span style="color:#397300">println</span>(<span style="color:#880000">"你好,仓颉!"</span>)
<strong>return</strong> <span style="color:#880000">0</span>
}
(* 注意:后续替换main.cj文件代码时,package demo保留)
(* 仓颉注释语法:// 符号之后写单行注释,也可以在一对 /* 和 */ 符号之间写多行注释)
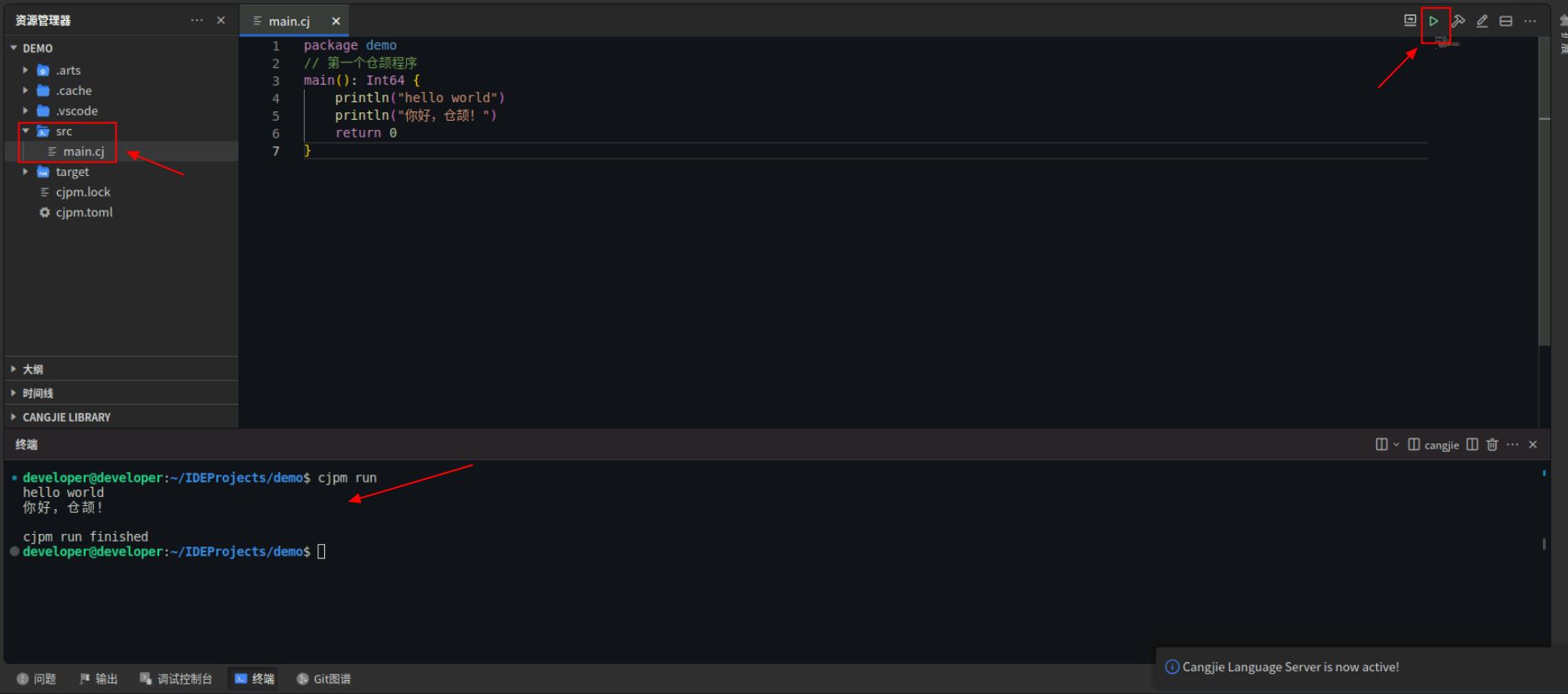
到这里,我们第一个仓颉程序就运行成功啦!后面案例中的示例代码都可以放到main.cj文件中进行执行,接下来我们继续探索仓颉语言。
3 枚举类型与模式匹配
3.1 枚举类型
enum 类型提供了通过列举一个类型的所有可能取值来定义此类型的方式。仓颉中的 enum 类型可以理解为函数式编程语言中的代数数据类型。
enum的定义:
定义 enum 时需要把它所有可能的取值一一列出,称这些值为 enum 的构造器(或者 constructor)。
具体代码如下:
<strong>enum</strong> <strong>RGBColor</strong> {
| Red | Green | Blue
}
enum 类型的定义以关键字 enum 开头,接着是 enum 的名字,之后是定义在一对花括号中的 enum 体,enum 体中定义了若干构造器,多个构造器之间使用 | 进行分隔。
enum 中的构造器还可以携带若干(至少一个)参数,称为有参构造器。
具体代码如下:
<strong>enum</strong> RGBColor {
| Red(<span style="color:#397300">UInt8</span>) | Green(<span style="color:#397300">UInt8</span>) | Blue(<span style="color:#397300">UInt8</span>)
}
仓颉支持同一个 enum 中定义多个同名构造器。
具体代码如下:
<strong>enum</strong> RGBColor {
| Red | Green | Blue
| Red(<span style="color:#397300">UInt8</span>) | Green(<span style="color:#397300">UInt8</span>) | Blue(<span style="color:#397300">UInt8</span>)
}
注意:enum只能定义在源文件的顶层作用域。
enum的使用:
具体代码如下:
<strong>enum</strong> <strong>RGBColor</strong> {
| <strong>Red</strong> | <strong>Green</strong> | <strong>Blue</strong>(<strong>UInt8</strong>)
}
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> r = <strong>RGBColor</strong>.<span>Red</span>
<strong>let</strong> g = <strong>Green</strong>
<strong>let</strong> b = <strong>Blue</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">100</span>)
}
可以省略类型名,但是可能类型名、变量名、函数名发生冲突,建议使用enum 类型名来使用 enum 构造器。
3.2 Option类型
Option 类型使用 enum 定义,它包含两个构造器:Some 和 None。
其中,Some 会携带一个参数,表示有值,None 不带参数,表示无值。当需要表示某个类型可能有值,也可能没有值的时候,可选择使用 Option 类型。
Option 类型被定义为一个泛型 enum 类型,具体代码如下:
enum Option<span style="color:#ab5656"><</span>
<span style="color:#397300">T</span>
<span style="color:#ab5656">></span> <span style="color:rgba(68, 68, 68, 0.667)">{</span>
<span style="color:#ab5656">|</span> Some<span style="color:rgba(68, 68, 68, 0.667)">(</span>
<span style="color:#397300">T</span>
<span style="color:rgba(68, 68, 68, 0.667)">)</span>
<span style="color:#ab5656">|</span> None
<span style="color:rgba(68, 68, 68, 0.667)">}</span>
其中,Some 构造器的参数类型就是类型形参 T,当 T 被实例化为不同的类型时,会得到不同的 Option 类型,例如:Option
Option 类型还有一种简单的写法:在类型名前加 ?。
例如,?Int64 等价于 Option
具体代码操作如下:
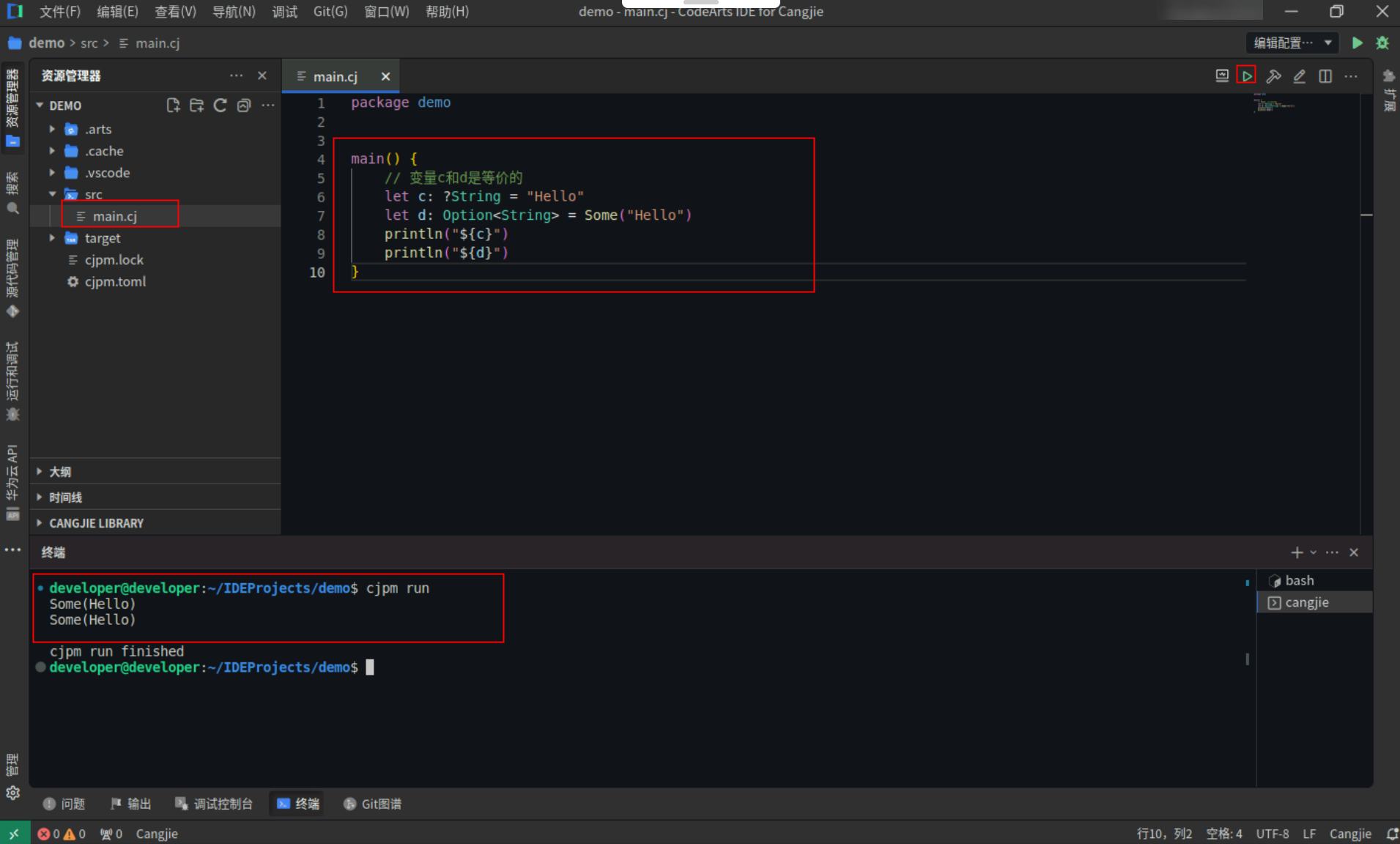
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<strong>main</strong>() {
<span style="color:#697070">// 变量c和d是等价的</span>
<strong>let</strong> <span>c</span>: ?<strong>String</strong> = <span style="color:#880000">"Hello"</span>
<strong>let</strong> <span>d</span>: <strong>Option</strong><<strong>String</strong>> = <strong>Some</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"Hello"</span>)
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"${c}"</span>)
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"${d}"</span>)
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
3.3 match表达式
match表达式的定义:
仓颉支持两种 match 表达式,第一种是包含待匹配值的 match 表达式,第二种是不含待匹配值的 match 表达式。
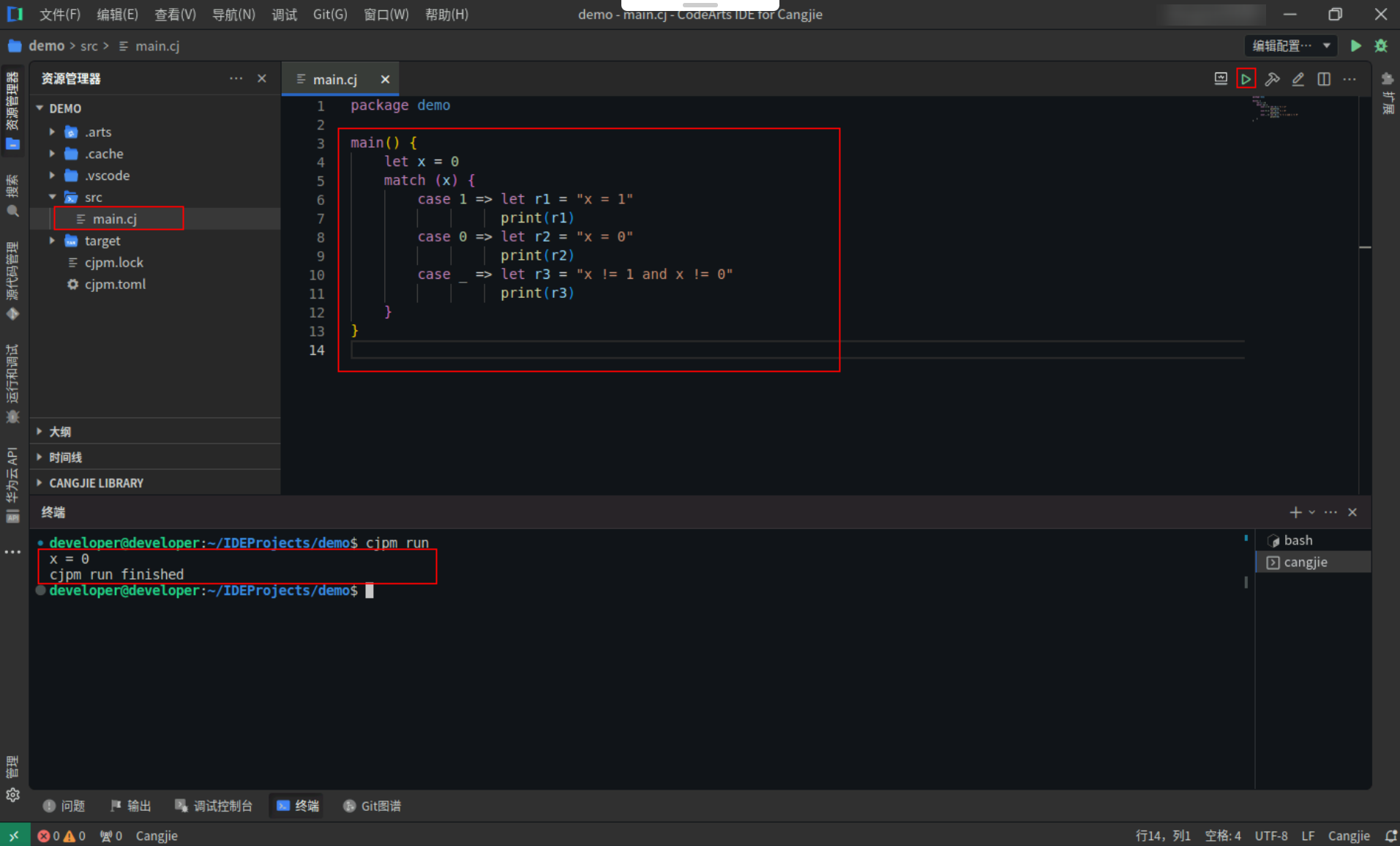
含匹配值的match表达式,下例中,因为 x 的值等于 0,所以会和第二条 case 分支匹配,最后输出 x = 0。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<span><strong>main</strong></span>() {
<span style="color:#397300">let</span> x = 0
match (x) {
<strong>case</strong> 1 => <span style="color:#397300">let</span> r1 = <span style="color:#880000">"x = 1"</span>
<span style="color:#397300">print</span>(r1)
<strong>case</strong> 0 => <span style="color:#397300">let</span> r2 = <span style="color:#880000">"x = 0"</span>
<span style="color:#397300">print</span>(r2)
<strong>case</strong> _ => <span style="color:#397300">let</span> r3 = <span style="color:#880000">"x != 1 and x != 0"</span>
<span style="color:#397300">print</span>(r3)
}
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
备注:终端窗口打印的内容,若存在警告信息,忽略即可,不影响程序运行。
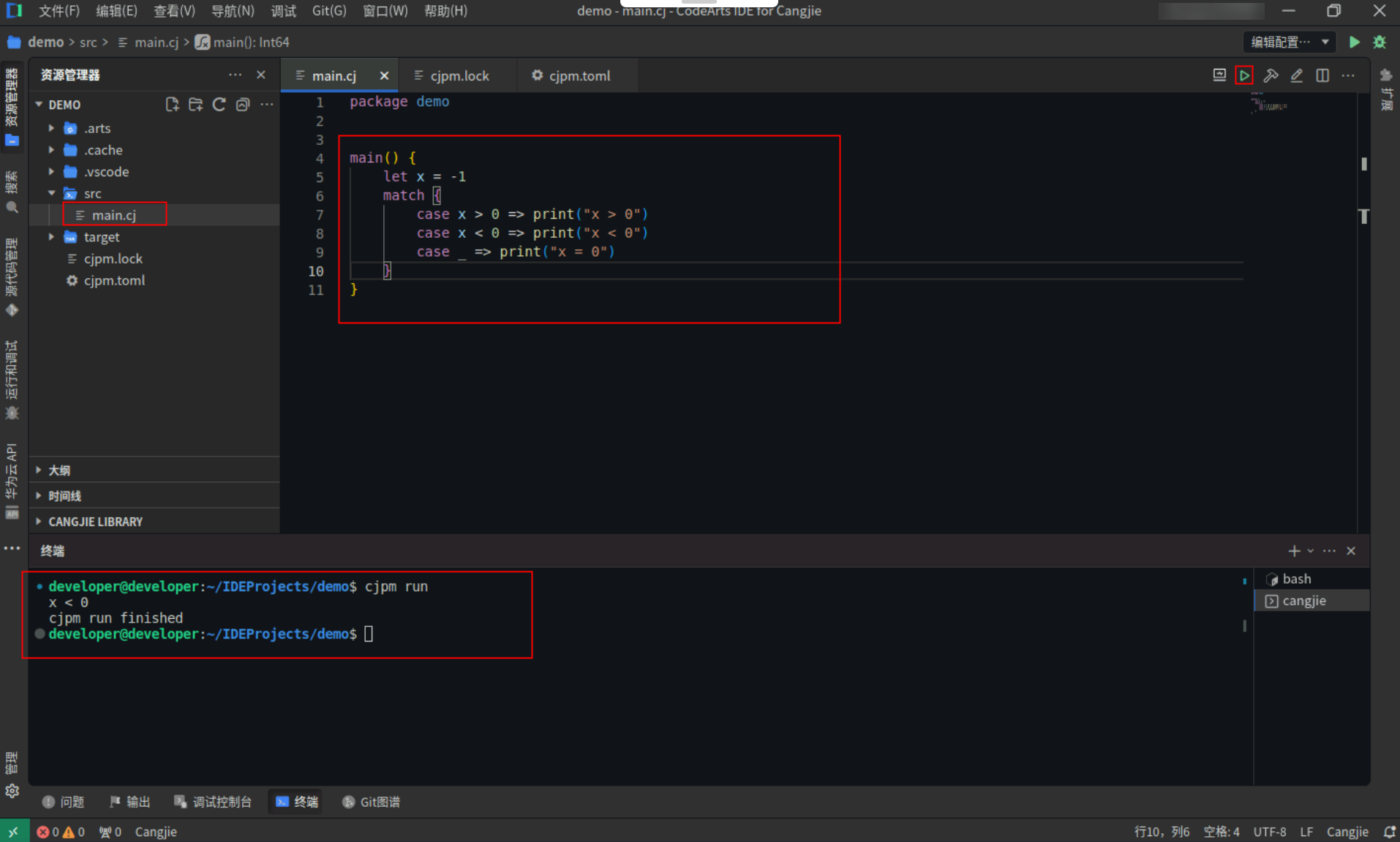
没有匹配值的match表达式,下例中,因为 x 的值等于 -1,所以第二条 case 分支中的表达式(即 x < 0)的值等于 true,执行 print("x < 0")。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<span><strong>main</strong></span>() {
<span style="color:#397300">let</span> x = -1
match {
<strong>case</strong> x > 0 => <span style="color:#397300">print</span>(<span style="color:#880000">"x > 0"</span>)
<strong>case</strong> x < 0 => <span style="color:#397300">print</span>(<span style="color:#880000">"x < 0"</span>)
<strong>case</strong> _ => <span style="color:#397300">print</span>(<span style="color:#880000">"x = 0"</span>)
}
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
备注:终端窗口打印的内容,若存在警告信息,忽略即可,不影响程序运行。
3.4 模式概述
对于包含匹配值的 match 表达式,case 之后支持哪些模式决定了 match 表达式的表达能力,本节中将依次介绍仓颉支持的模式,包括:常量模式、通配符模式、绑定模式、tuple 模式、类型模式和 enum 模式。
常量模式:
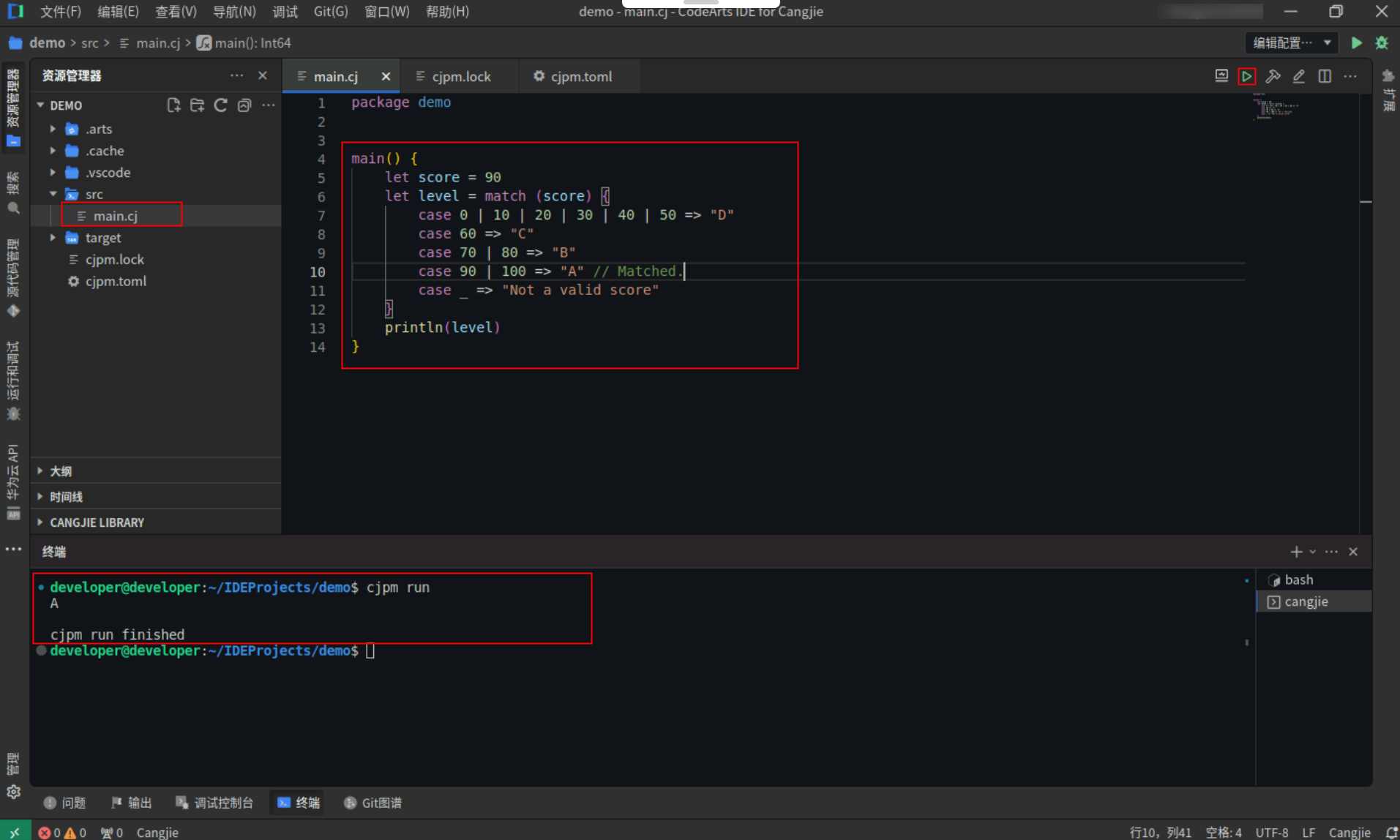
下面的例子中,根据 score 的值(假设 score 只能取 0 到 100 间被 10 整除的值),输出考试成绩的等级。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> score = <span style="color:#880000">90</span>
<strong>let</strong> level = match (score) {
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">0</span> | <span style="color:#880000">10</span> | <span style="color:#880000">20</span> | <span style="color:#880000">30</span> | <span style="color:#880000">40</span> | <span style="color:#880000">50</span> => <span style="color:#880000">"D"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">60</span> => <span style="color:#880000">"C"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">70</span> | <span style="color:#880000">80</span> => <span style="color:#880000">"B"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">90</span> | <span style="color:#880000">100</span> => <span style="color:#880000">"A"</span> <span style="color:#697070">// Matched.</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span><span>_</span> =></span> <span style="color:#880000">"Not a valid score"</span>
}
<strong>println</strong>(level)
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
备注:终端窗口打印的内容,若存在警告信息,忽略即可,不影响程序运行。
通配符模式:
通配符模式使用下划线 _ 表示,可以匹配任意值。通配符模式通常作为最后一个 case 中的模式,用来匹配其他 case 未覆盖到的情况,如常量模式中匹配 score 值的示例中,最后一个 case 中使用 _ 来匹配无效的 score 值。
绑定模式:
绑定模式使用 id 表示,id 是一个合法的标识符。与通配符模式相比,绑定模式同样可以匹配任意值,但绑定模式会将匹配到的值与 id 进行绑定,在 => 之后可以通过 id 访问其绑定的值。
下面的例子中,最后一个 case 中使用了绑定模式,用于绑定非 0 值。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> x = -<span style="color:#880000">10</span>
<strong>let</strong> y = match (x) {
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">0</span> => <span style="color:#880000">"zero"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span><span>n</span> =></span> <span style="color:#880000">"x is not zero and x = ${n}"</span>
}
<strong>println</strong>(y)
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
备注:终端窗口打印的内容,若存在警告信息,忽略即可,不影响程序运行。
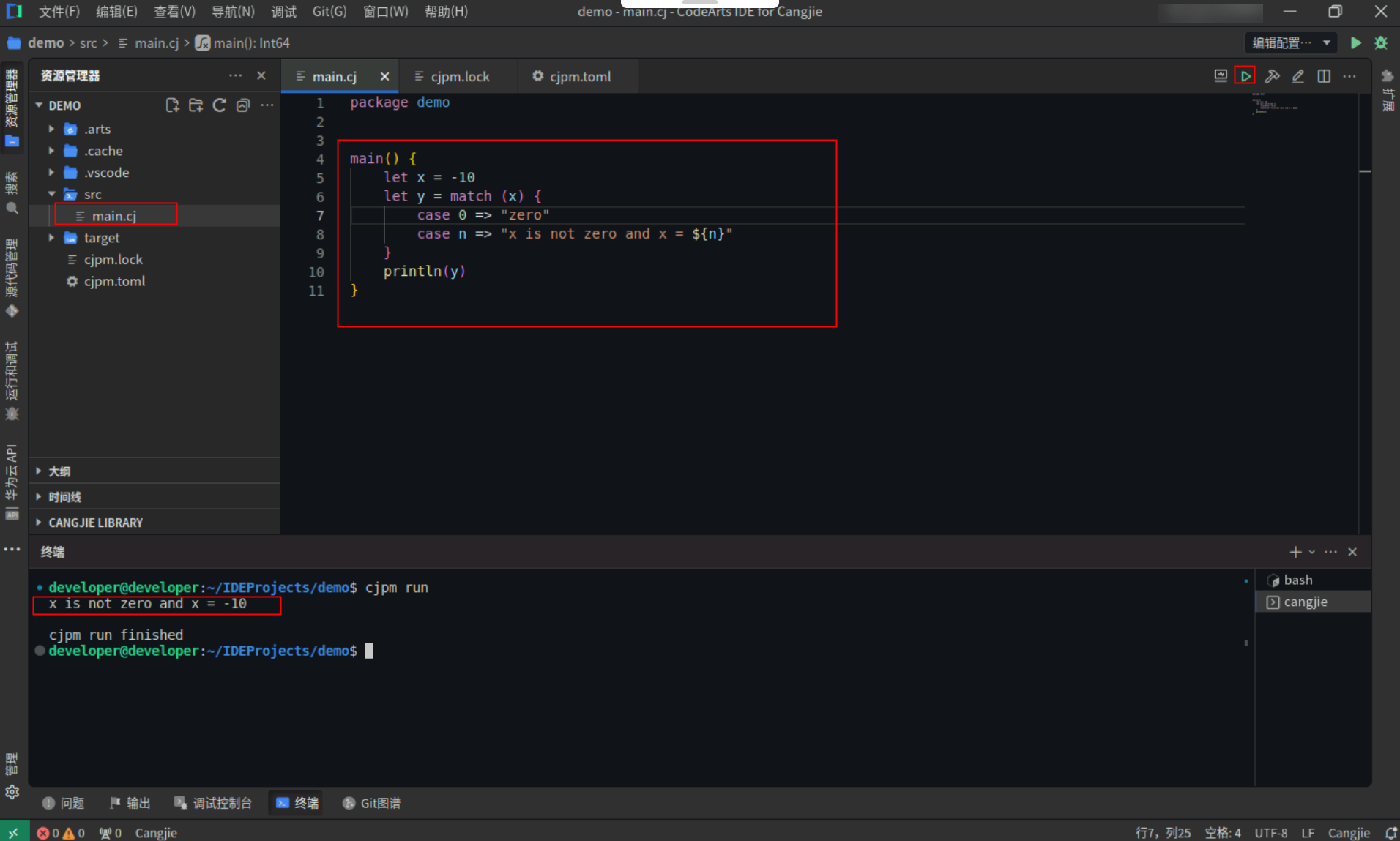
Tuple模式:
Tuple 模式用于 tuple 值的匹配,它的定义和 tuple 字面量类似:(p_1, p_2, …, p_n),区别在于这里的 p_1 到 p_n(n 大于等于 2)是模式而不是表达式。
tuple模式使用,具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> tv = (<span style="color:#880000">"Alice"</span>, <span style="color:#880000">24</span>)
<strong>let</strong> s = match (tv) {
<strong>case</strong> <span>(<span><span style="color:#880000">"Bob"</span>, age</span>) =></span> <span style="color:#880000">"Bob is ${age} years old"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span>(<span><span style="color:#880000">"Alice"</span>, age</span>) =></span> <span style="color:#880000">"Alice is ${age} years old"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span>(<span>name, <span style="color:#880000">100</span></span>) =></span> <span style="color:#880000">"${name} is 100 years old"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span>(<span>_, _</span>) =></span> <span style="color:#880000">"someone"</span>
}
<strong>println</strong>(s)
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
备注:终端窗口打印的内容,若存在警告信息,忽略即可,不影响程序运行。
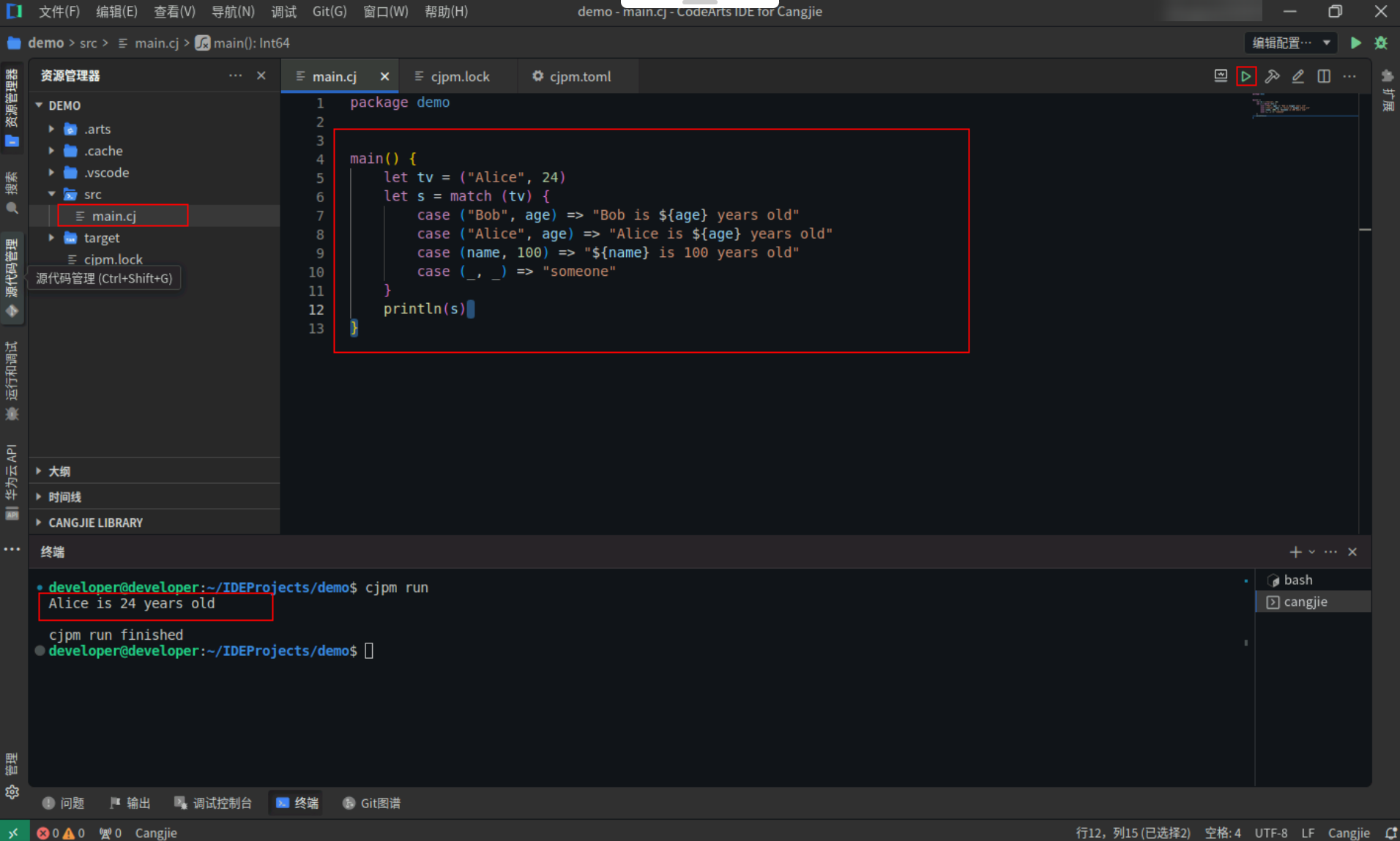
类型模式:
类型模式用于判断一个值的运行时类型是否是某个类型的子类型。
假设有如下两个类,Base 和 Derived,并且 Derived 是 Base 的子类,Base 的无参构造函数中将 a 的值设置为 10,Derived 的无参构造函数中将 a 的值设置为 20。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
open <strong>class</strong> <strong>Base</strong> {
<strong>var</strong> <span>a</span>: <strong>Int64</strong>
<strong>public</strong> <strong>init</strong>() {
a = <span style="color:#880000">10</span>
}
}
<strong>class</strong> <strong>Derived</strong> <: <strong>Base</strong> {
<strong>public</strong> <strong>init</strong>() {
a = <span style="color:#880000">20</span>
}
}
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>var</strong> d = <strong>Derived</strong>()
<strong>var</strong> r = match (d) {
<strong>case</strong> <span>b</span>: <span><span>Base</span> =></span> b.<span>a</span> <span style="color:#697070">// Matched.</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span><span>_</span> =></span> <span style="color:#880000">0</span>
}
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"r = ${r}"</span>)
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
备注:终端窗口打印的内容,若存在警告信息,忽略即可,不影响程序运行。
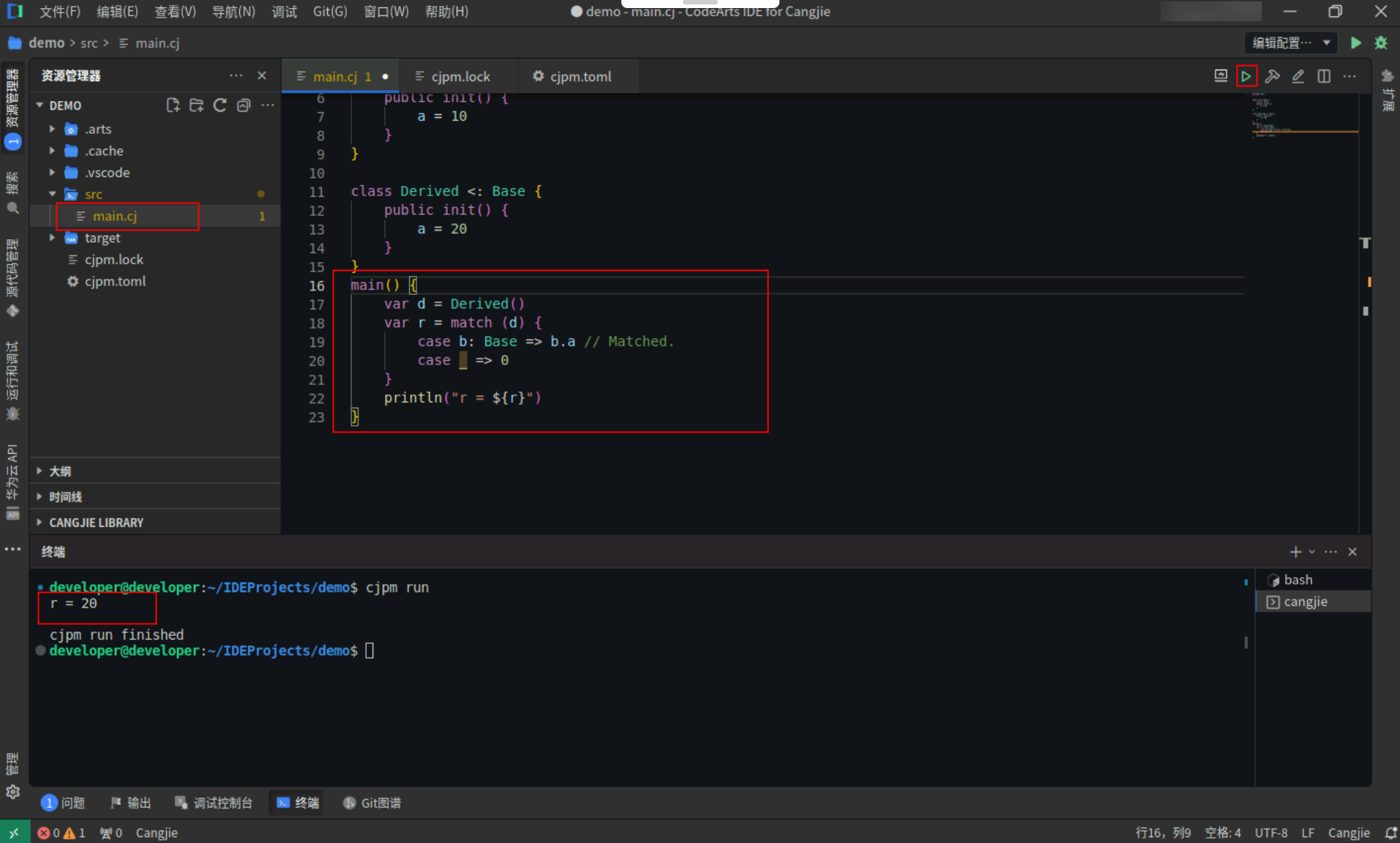
enum模式:
enum 模式用于匹配 enum 类型的实例,它的定义和 enum 的构造器类似:无参构造器 C 或有参构造器 C(p_1, p_2, …, p_n),构造器的类型前缀可以省略,区别在于这里的 p_1 到 p_n(n 大于等于 1)是模式。
下例中,展示了 enum 模式的使用,因为 x 的构造器是 Year,所以会和第一个case匹配,具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<strong>enum</strong> <strong>TimeUnit</strong> {
<span style="color:#ab5656">|</span> <span style="color:#880000">Year</span>(<span style="color:#880000">UInt64</span>)
<span style="color:#ab5656">|</span> <span style="color:#880000">Month</span>(<span style="color:#880000">UInt64</span>)
}
main() {
<strong>let</strong> x <span style="color:#ab5656">=</span> <span style="color:#880000">Year</span>(<span style="color:#880000">2</span>)
<strong>let</strong> s <span style="color:#ab5656">=</span> match (x) {
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">Year</span>(n) <span style="color:#ab5656">=></span> <span style="color:#880000">"x has ${n * 12} months"</span> <span style="color:#697070">// Matched.</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">TimeUnit</span>.<span style="color:#880000">Month</span>(n) <span style="color:#ab5656">=></span> <span style="color:#880000">"x has ${n} months"</span>
}
println(s)
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
备注:终端窗口打印的内容,若存在警告信息,忽略即可,不影响程序运行。
模式的嵌套组合:
Tuple 模式和 enum 模式可以嵌套任意模式。
下面的代码展示了不同模式嵌套组合使用,具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<strong>enum</strong> <strong>TimeUnit</strong> {
| <strong>Year</strong>(<strong>UInt64</strong>)
| <strong>Month</strong>(<strong>UInt64</strong>)
}
<strong>enum</strong> <strong>Command</strong> {
| <strong>SetTimeUnit</strong>(<strong>TimeUnit</strong>)
| <strong>GetTimeUnit</strong>
| <strong>Quit</strong>
}
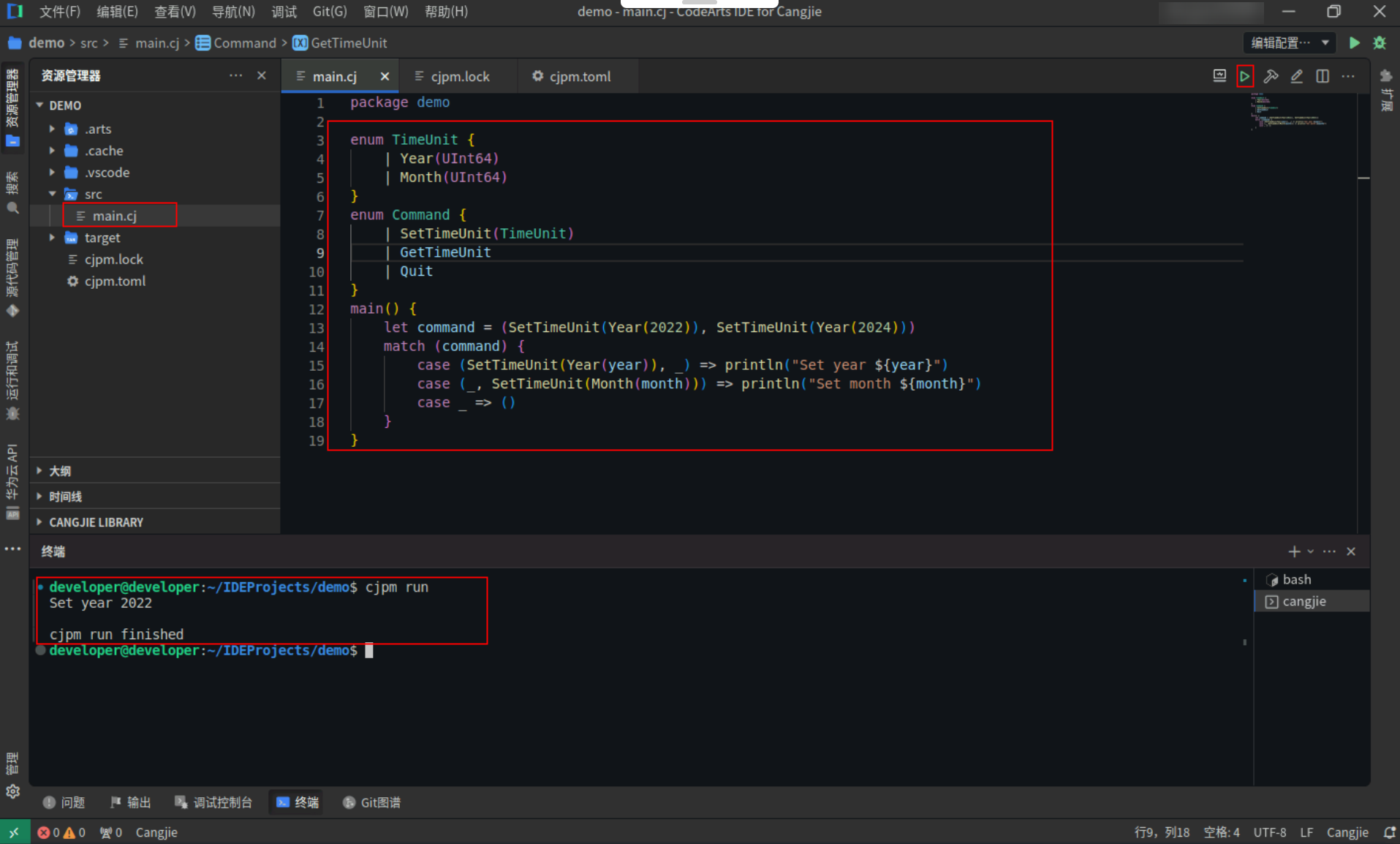
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> command = (<strong>SetTimeUnit</strong>(<strong>Year</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">2022</span>)), <strong>SetTimeUnit</strong>(<strong>Year</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">2024</span>)))
match (command) {
<strong>case</strong> <span>(<span>SetTimeUnit(Year(year)), _</span>) =></span> <strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"Set year ${year}"</span>)
<strong>case</strong> <span>(<span>_, SetTimeUnit(Month(month))</span>) =></span> <strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"Set month ${month}"</span>)
<strong>case</strong> <span><span>_</span> =></span> ()
}
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
3.5 模式的Refutability
备注:refutable 中文意思是可反驳的;irrefutable是不能反驳的,无可辩驳的。
模式可以分为两类:refutable 模式和 irrefutable 模式。在类型匹配的前提下,当一个模式有可能和待匹配值不匹配时,称此模式为 refutable 模式;反之,当一个模式总是可以和待匹配值匹配时,称此模式为 irrefutable 模式。
refutable 模式:常量模式、类型模式。
irrefutable 模式:通配符模式、绑定模式、Tuple 模式、enum 模式。
常量模式是 refutable 模式。例如,下例中第一个 case 中的 1 和第二个 case 中的 2 都有可能和 x 的值不相等。
具体代码如下:
func <strong>constPat</strong>(<span>x: Int64</span>) {
match (x) {
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">1</span> => <span style="color:#880000">"one"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span style="color:#880000">2</span> => <span style="color:#880000">"two"</span>
<strong>case</strong> <span><span>_</span> =></span> <span style="color:#880000">"_"</span>
}
}
绑定模式是 irrefutable 模式。例如,下例中无论 x 的值是多少,绑定模式 a 总能和其匹配,具体代码如下:
func <strong>varPat</strong>(<span>x: Int64</span>) {
match (x) {
<strong>case</strong> <span><span>a</span> =></span> <span style="color:#880000">"x = ${a}"</span>
}
}
3.6 if-let表达式
if-let 表达式首先对条件中 <- 右侧的表达式进行求值,如果此值能匹配 <- 左侧的模式,则执行 if 分支,否则执行 else 分支(可省略)。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
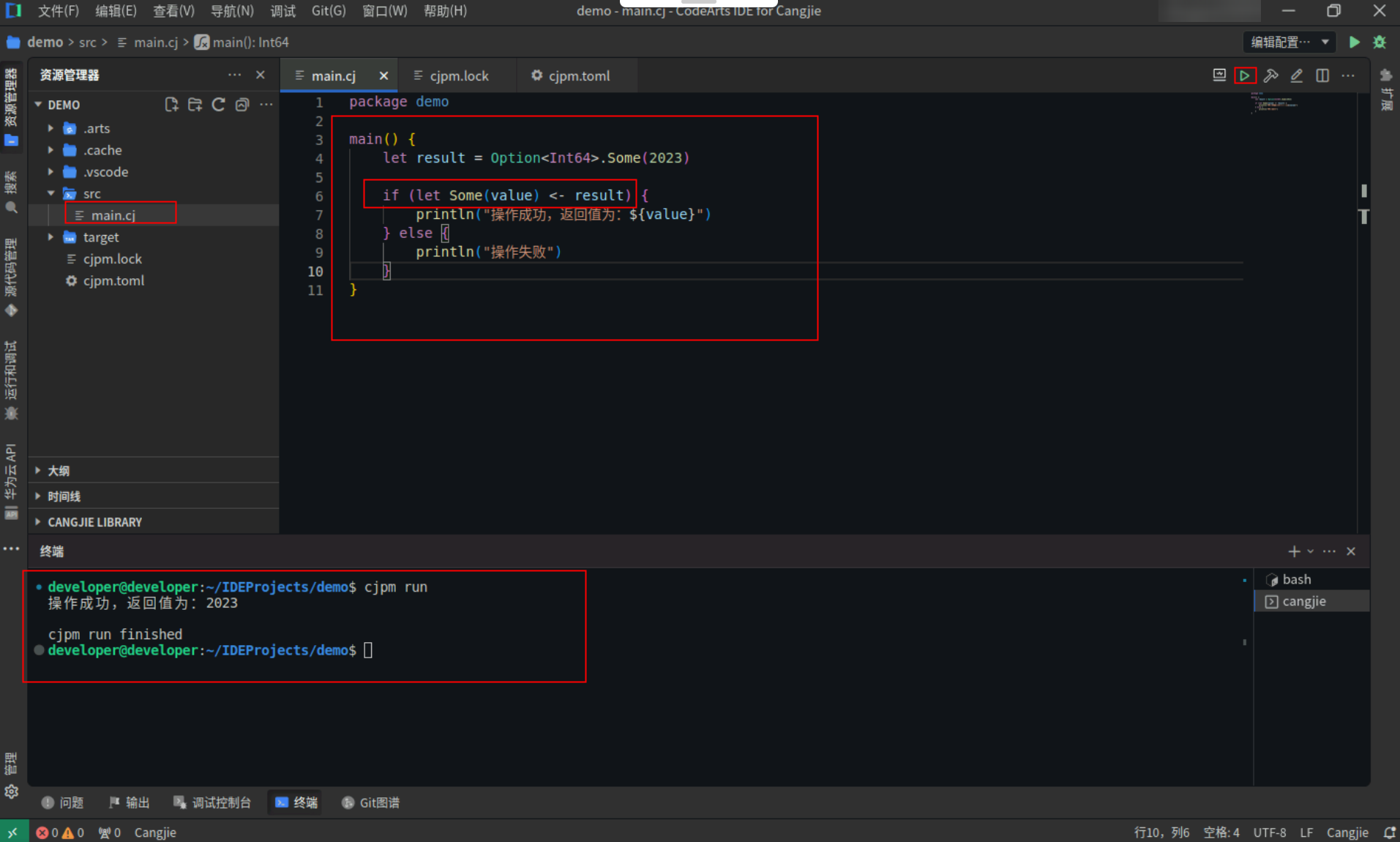
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> result = <strong>Option</strong><<strong>Int64</strong>>.<strong>Some</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">2023</span>)
<strong>if</strong> (<strong>let</strong> <strong>Some</strong>(value) <- result) {
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"操作成功,返回值为:${value}"</span>)
} <strong>else</strong> {
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"操作失败"</span>)
}
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
3.7 while-let表达式
while-let 表达式首先对条件中 <- 右侧的表达式进行求值,如果此值能匹配 <- 左侧的模式,则执行循环体,然后重复执行此过程。如果模式匹配失败,则结束循环,继续执行 while-let 表达式之后的代码。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
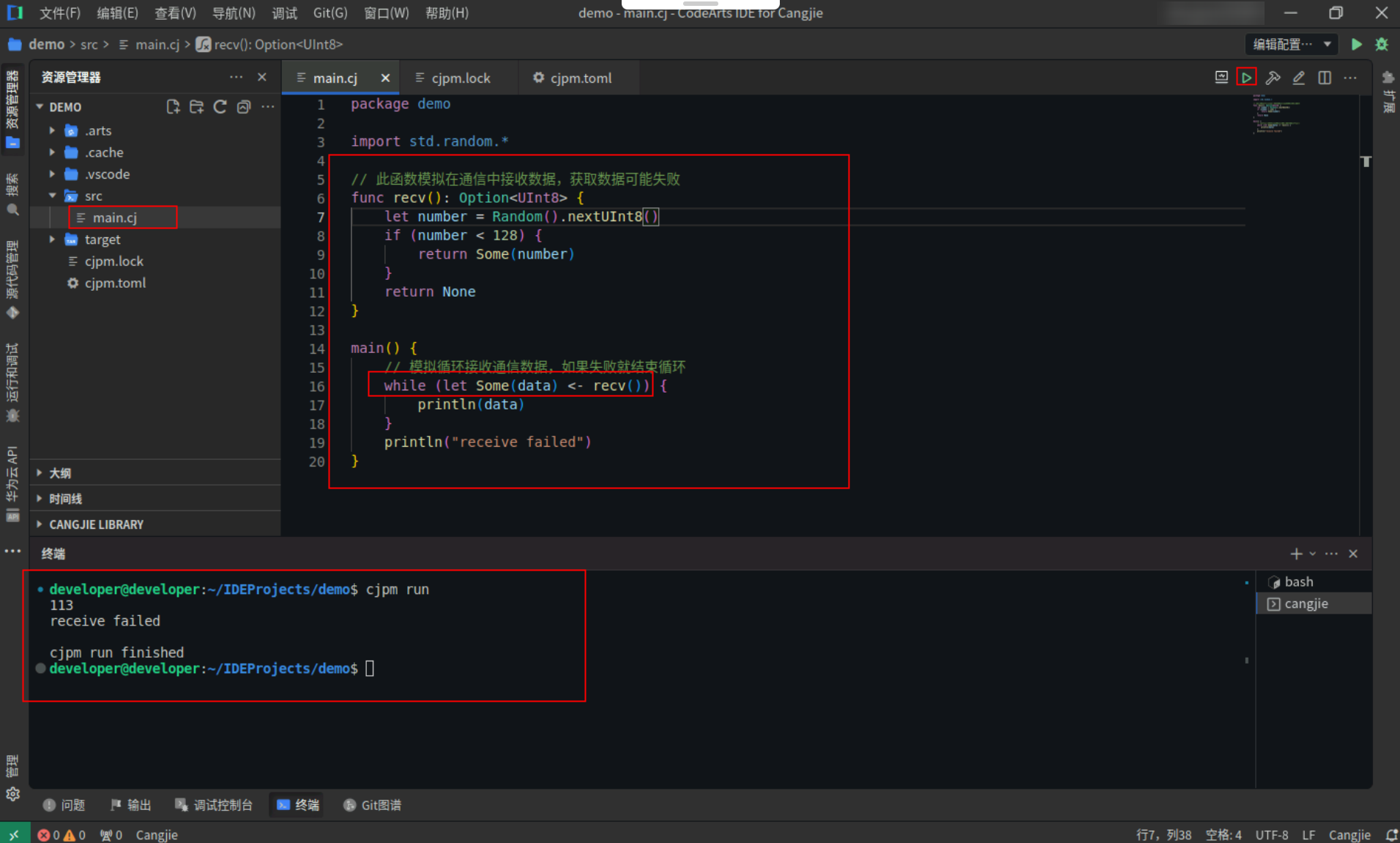
<strong>import</strong> std.<span>random</span>.*
<span style="color:#697070">// 此函数模拟在通信中接收数据,获取数据可能失败</span>
func <strong>recv</strong>(): <strong>Option</strong><<strong>UInt8</strong>> {
<strong>let</strong> <span style="color:#397300">number</span> = <strong>Random</strong>().<strong>nextUInt8</strong>()
<strong>if</strong> (<span style="color:#397300">number</span> < <span style="color:#880000">128</span>) {
<strong>return</strong> <strong>Some</strong>(<span style="color:#397300">number</span>)
}
<strong>return</strong> <strong>None</strong>
}
<strong>main</strong>() {
<span style="color:#697070">// 模拟循环接收通信数据,如果失败就结束循环</span>
<strong>while</strong> (<strong>let</strong> <strong>Some</strong>(data) <- <strong>recv</strong>()) {
<strong>println</strong>(data)
}
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"receive failed"</span>)
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可能打印出以下内容。
备注:由于使用了Random函数,每次运行结果可能不一样。
3.8 其他使用模式的地方
模式除了可以在 match 表达式中使用外,还可以使用在变量定义和 for in 表达式中。但是,并不是所有的模式都能使用在变量定义和 for in 表达式中,只有 irrefutable 的模式才能在这两处被使用,所以只有通配符模式、绑定模式、irrefutable tuple 模式和 irrefutable enum 模式是允许的。
- 变量定义和 for in 表达式中使用通配符模式。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
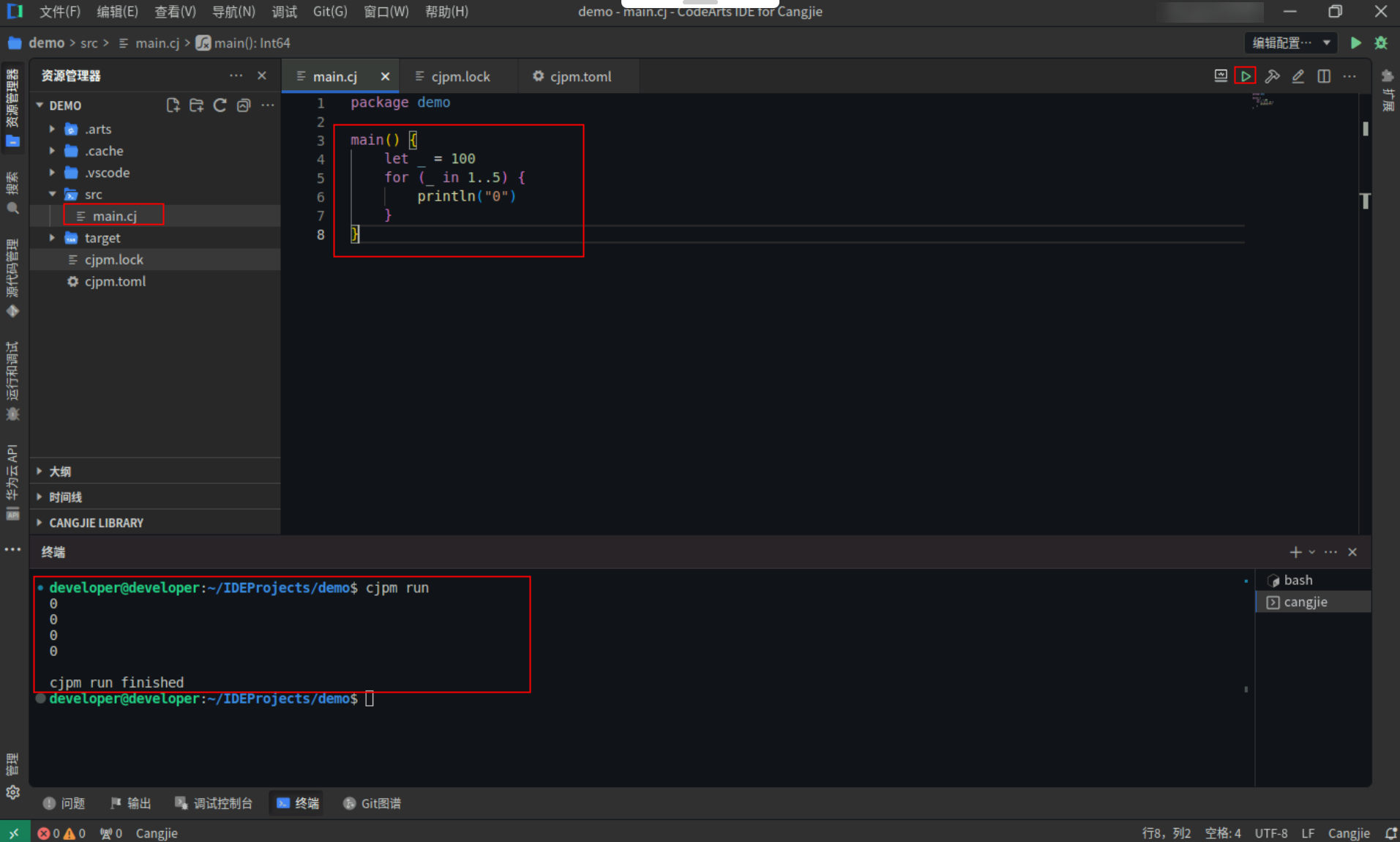
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> _ = <span style="color:#880000">100</span>
<strong>for</strong> (_ <strong>in</strong> <span style="color:#880000">1.</span>
<span style="color:#880000">.5</span>) {
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"0"</span>)
}
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
-
变量定义和 for in 表达式中使用绑定模式。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> x = <span style="color:#880000">100</span>
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"x = ${x}"</span>)
<strong>for</strong> (i <strong>in</strong> <span style="color:#880000">1.</span>
<span style="color:#880000">.5</span>) {
<strong>println</strong>(i)
}
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
-
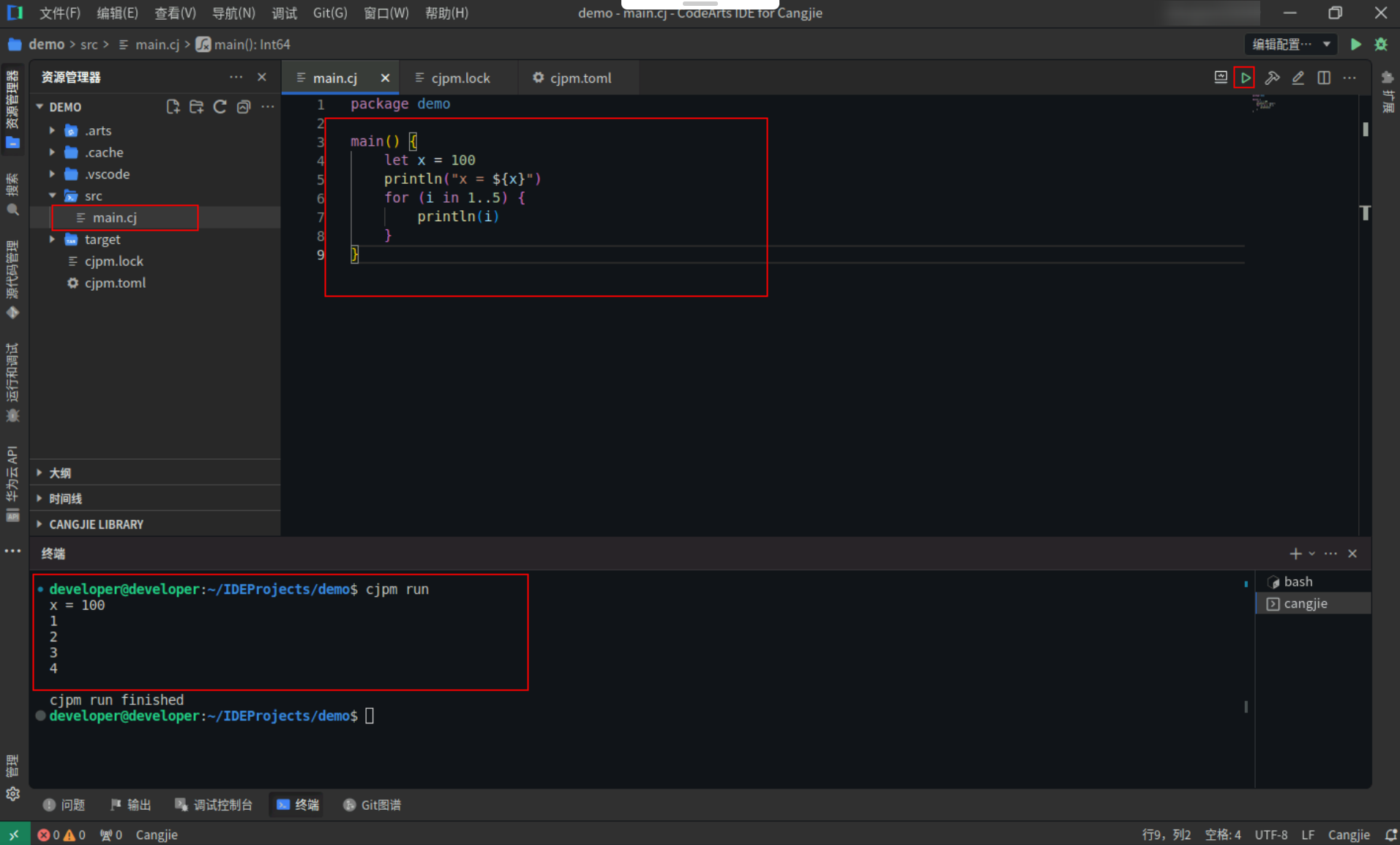
变量定义和 for in 表达式中使用 irrefutable tuple 模式。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<span><strong>main</strong></span>() {
<span style="color:#397300">let</span> (x, y) = (100, 200)
println(<span style="color:#880000">"x = <span style="color:#ab5656">${x}</span>"</span>)
println(<span style="color:#880000">"y = <span style="color:#ab5656">${y}</span>"</span>)
<strong>for</strong> ((i, j) in [(<span style="color:#880000">1</span>, <span style="color:#880000">2</span>), (<span style="color:#880000">3</span>, <span style="color:#880000">4</span>), (<span style="color:#880000">5</span>, <span style="color:#880000">6</span>)]) {
println("Sum = <span style="color:#ab5656">${i + j}</span>")
}
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
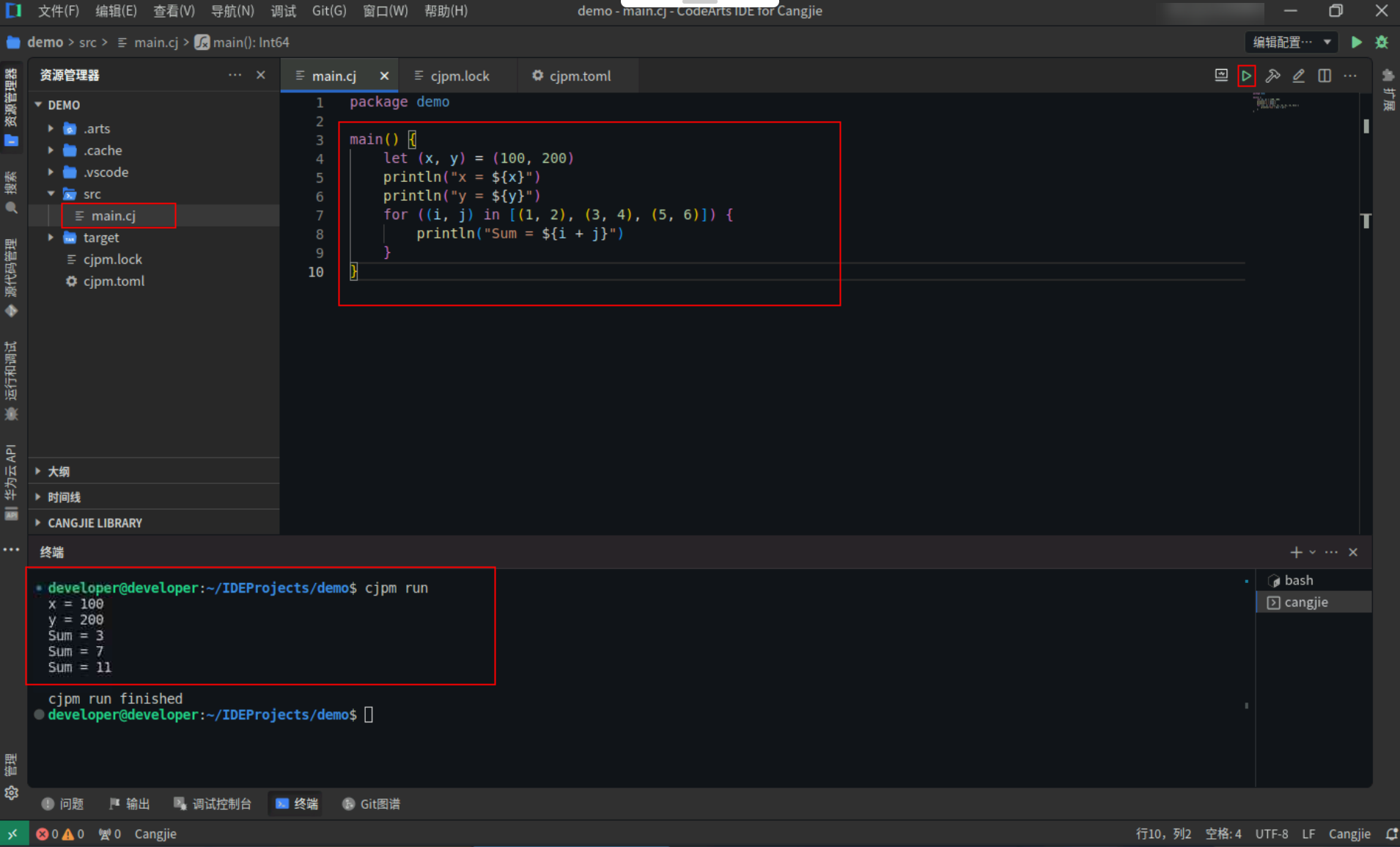
-
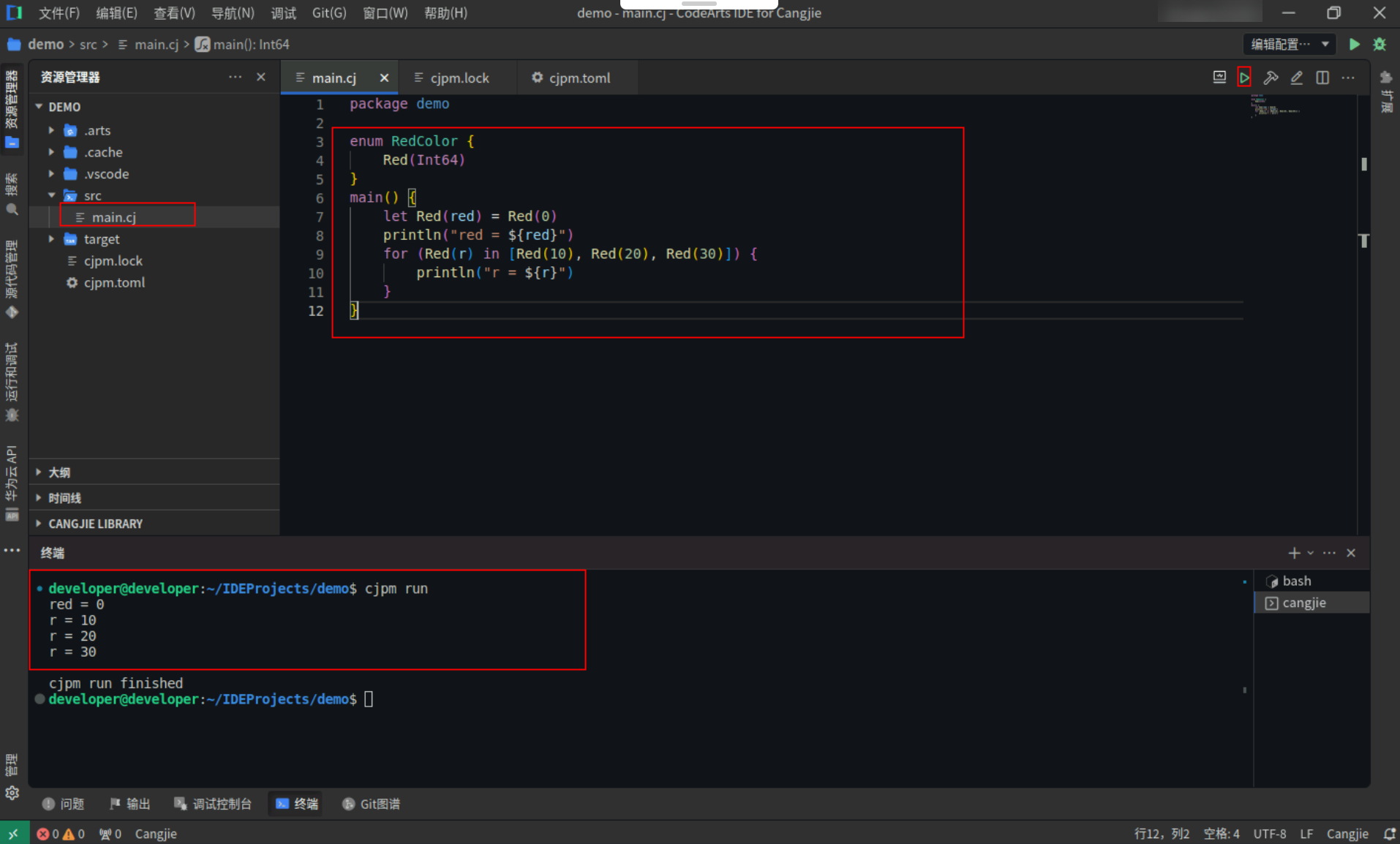
变量定义和 for in 表达式中使用 irrefutable enum 模式。
具体代码操作如下:
Step1:复制以下代码,替换main.cj文件中的代码。(保留package)
<strong>enum</strong> <strong>RedColor</strong> {
<strong>Red</strong>(<strong>Int64</strong>)
}
<strong>main</strong>() {
<strong>let</strong> <strong>Red</strong>(red) = <strong>Red</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">0</span>)
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"red = ${red}"</span>)
<strong>for</strong> (<strong>Red</strong>(r) <strong>in</strong> [<strong>Red</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">10</span>), <strong>Red</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">20</span>), <strong>Red</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">30</span>)]) {
<strong>println</strong>(<span style="color:#880000">"r = ${r}"</span>)
}
}
Step2:点击编辑器右上角运行按钮直接运行,终端窗口可以看到打印内容。
至此,仓颉之枚举类型与模式匹配的冒险之旅案例内容已全部完成。
如果想了解更多仓颉编程语言知识可以访问:https://cangjie-lang.cn/
</div>相关推荐
- 「第三届开放原子大赛」获奖队伍专访来啦!企业篇
- 从本体论到落地实践:制造业数字化转型的核心逻辑与工具选择 | 葡萄城技术团队
- 轻松搞定Excel公式错误:SpreadJS让表格开发不再头疼 | 葡萄城技术团队
- vivo GPU容器与 AI 训练平台探索与实践
- SQLShift V6.0 发布!函数迁移&达梦适配一步到位!
- Oinone × AI Agent 落地指南:别让 AI Agent 负责“转账”:用神经-符号混合架构把它从 Demo 拉进生产
- 借助 Okta 和 NGINX Ingress Controller 实现 K8s OpenID Connect 身份验证
- 同样是低代码,为什么有人扩容有人烂尾?答案藏在交付体系里-拆解 Oinone 的交付底座



